| Gene Symbol | ATP6V0A4 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 50617 |
| Full Name | ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 |
| Synonyms | A4,ATP6N1B,ATP6N2,RDRTA2,RTA1C,RTADR,STV1,VPH1,VPP2 |
| General protein information |
|
| Gene Type | protein-coding |
| Organism | Homo sapiens(human) |
| Genome | |
| Summary | This gene encodes a component of vacuolar ATPase (V-ATPase), a multisubunit enzyme that mediates acidification of intracellular compartments of eukaryotic cells. V-ATPase dependent acidification is necessary for such intracellular processes as protein sorting, zymogen activation, receptor-mediated endocytosis, and synaptic vesicle proton gradient generation. V-ATPase is composed of a cytosolic V1 domain and a transmembrane V0 domain. The V1 domain consists of three A and three B subunits, two G subunits plus the C, D, E, F, and H subunits. The V1 domain contains the ATP catalytic site. The V0 domain consists of five different subunits: a, c, c', c'', and d. This gene is one of four genes in man and mouse that encode different isoforms of the a subunit. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding the same protein have been described. Mutations in this gene are associated with renal tubular acidosis associated with preserved hearing. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
| Disorder MIM: | |
| Disorder Html: | Renal tubular acidosis, distal, autosomal recessive, 602722 (3) |
-
REAGENT SERVICES
Hot!
-
Most Popular Services
-
Molecular Biology
-
Recombinant Antibody/Protein
-
Reagent Antibody
-
CRISPR Gene Editing
-
DNA Mutant Library
-
IVT RNA and LNP Formulations
-
Oligo Synthesis
-
Peptides
-
Cell Engineering
-
- Gene Synthesis FLASH Gene
- GenBrick™ Up to 200kb
- Gene Fragments Up to 3kb now
- Plasmid DNA Preparation Upgraded
- Cloning and Subcloning
- ORF cDNA Clones
- mRNA Plasmid Solutions New!
- Cell free mRNA Template New!
- AAV Plasmid Solutions New!
- Mutagenesis
- GenCircle™ Double-Stranded DNA New!
- GenSmart™ Online Tools
-
-
PRODUCTS
-
Most Popular Reagents
-
 Instruments
Instruments
-
Antibodies
-
ELISA Kits
-
Protein Electrophoresis and Blotting
-
Protein and Antibody Purification
-
Recombinant Proteins
-
Molecular Biology
-
Stable Cell Lines
-
Cell Isolation and Activation
-
 IVD Raw Materials
IVD Raw Materials
-
 Therapy Applications
Therapy Applications
-
Resources
-
- All Instruments
- Automated Protein and Antibody Purification SystemNew!
- Automated Plasmid MaxiprepHot!
- Automated Plasmid/Protein/Antibody Mini-scale Purification
- eBlot™ Protein Transfer System
- eStain™ Protein Staining System
- eZwest™ Lite Automated Western Blotting Device
- CytoSinct™ 1000 Cell Isolation Instrument
-
- Pharmacokinetics and Immunogenicity ELISA Kits
- Viral Titration QC ELISA Kits
- -- Lentivirus Titer p24 ELISA KitHot!
- -- MuLV Titer p30 ELISA KitNew!
- -- AAV2 and AAVX Titer Capsid ELISA Kits
- Residual Detection ELISA Kits
- -- T7 RNA Polymerase ELISA KitNew!
- -- BSA ELISA Kit, 2G
- -- Cas9 ELISA KitHot!
- -- Protein A ELISA KitHot!
- -- His tagged protein detection & purification
- dsRNA ELISA Kit
- Endonuclease ELISA Kit
- COVID-19 Detection cPass™ Technology Kits
-
- Automated Maxi-Plasmid PurificationHot!
- Automated Mini-Plasmid PurificationNew!
- PCR Reagents
- S.marcescens Nuclease Benz-Neburase™
- DNA Assembly GenBuilder™
- Cas9 / Cas12a / Cas13a Nucleases
- Base and Prime Editing Nucleases
- GMP Cas9 Nucleases
- CRISPR sgRNA Synthesis
- HDR Knock-in Template
- CRISPR Gene Editing Kits and Antibodies
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Anti-Camelid VHH]() MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
-
![ELISA Kits]() ELISA Kits
ELISA Kits
-
![Precast Gels]() SurePAGE™ Precast Gels
SurePAGE™ Precast Gels
-
![Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System]() AmMag™ Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System
AmMag™ Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System
-
![Target Proteins]() Target Proteins
Target Proteins
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Stable Cell Lines]() Stable Cell Lines
Stable Cell Lines
-
![Cell Isolation and Activation]() Cell Isolation and Activation
Cell Isolation and Activation
-
 IVD Raw Materials
IVD Raw Materials
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
- APPLICATIONS
- RESOURCES
- ABOUT US
- SIGN IN My Account SIGN OUT
- REGISTER
ORF » Species Summary » Homo sapiens » ATP6V0A4 cDNA ORF clone
ATP6V0A4 cDNA ORF clone, Homo sapiens(human)
-
Gene
-
Clones
gRNAs
-
Summary
-
mRNA and Protein(s)
mRNA Protein Name XM_005250393.1 XP_005250450.1 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform X1 XM_005250394.3 XP_005250451.1 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform X1 NM_130841.2 NP_570856.2 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 NM_020632.3 NP_065683.2 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 NM_020632.2 NP_065683.2 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 NM_130840.3 NP_570855.2 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 NM_130840.2 NP_570855.2 V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 -
Pathways from BioSystems

-
Homologies
Canis lupus familiaris (dog) ATP6V0A4 XP_539895.2 Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Atp6v0a4 NP_001100061.1 Pan troglodytes (chimpanzee) ATP6V0A4 XP_003318871.1 Bos taurus (cattle) ATP6V0A4 NP_001192780.1 Mus musculus (house mouse) Atp6v0a4 NP_536715.3 Xenopus tropicalis (tropical clawed frog) atp6v0a4 NP_001107162.1 Anopheles gambiae (African malaria mosquito) AgaP_AGAP001587 XP_321521.2 Gallus gallus (chicken) ATP6V0A4 NP_001073571.2 Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) VHA-A3 NP_568051.1 Arabidopsis thaliana (thale cress) VHA-A2 NP_179736.1 Oryza sativa (rice) Os03g0251500 NP_001049572.1 Homo sapiens (human) ATP6V0A4 NP_570856.2 Macaca mulatta (Rhesus monkey) ATP6V0A4 XP_002803521.1 Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) Vha100-2 NP_650722.1 -
Gene Ontology

-
Bibliography
Related articles in PubMed
Clinical and genetic analysis of distal renal tubular acidosis in three Chinese children.
Liu J, Shen Q, Li G, Zhai Y, Fang X, Xu H
Renal failure40(1)520-526(2018 Nov)Five Novel Mutations in Chinese Children with Primary Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis.
Zhang R, Wang C, Lang Y, Gao Y, Chen Z, Lu J, Zhao X, Shao L
Genetic testing and molecular biomarkers22(10)599-606(2018 Oct)Distal renal tubular acidosis in a Libyan patient: Evidence for digenic inheritance.
Nagara M, Papagregoriou G, Ben Abdallah R, Landoulsi Z, Bouyacoub Y, Elouej S, Kefi R, Pippucci T, Voskarides K, Bashamboo A, McElreavey K, Hachicha M, Romeo G, Seri M, Deltas C, Abdelhak S
European journal of medical genetics61(1)1-7(2018 Jan)The genetic and clinical spectrum of a large cohort of patients with distal renal tubular acidosis.
Palazzo V, Provenzano A, Becherucci F, Sansavini G, Mazzinghi B, Orlandini V, Giunti L, Roperto RM, Pantaleo M, Artuso R, Andreucci E, Bargiacchi S, Traficante G, Stagi S, Murer L, Benetti E, Emma F, Giordano M, Rivieri F, Colussi G, Penco S, Manfredini E, Caruso MR, Garavelli L, Andrulli S, Vergine G, Miglietti N, Mancini E, Malaventura C, Percesepe A, Grosso E, Materassi M, Romagnani P, Giglio S
Kidney international91(5)1243-1255(2017 05)GeneRIFs: Gene References Into Functions What's a GeneRIF?
The following ATP6V0A4 gene cDNA ORF clone sequences were retrieved from the NCBI Reference Sequence Database (RefSeq). These sequences represent the protein coding region of the ATP6V0A4 cDNA ORF which is encoded by the open reading frame (ORF) sequence. ORF sequences can be delivered in our standard vector, pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK or the vector of your choice as an expression/transfection-ready ORF clone. Not the clone you want? Click here to find your clone.

Online Only Promotion
Up to 50% OFF! Starting
from $49/clone-
Reference Sequences (Refseq)
CloneID OHu15055 
Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version NM_020632.2 Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1506873600000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from DB230144.1, BC109305.1, AF245517.1 and BC109304.1. This sequence is a reference standard in the RefSeqGene project. On Jan 19, 2006 this sequence version replaced NM_020632.1. Transcript Variant: This variant (1) is the longest transcript. Variants 1, 2, and 3 encode the same protein. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: AF245517.1, AK292945.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1968832, SAMEA1968968 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## COMPLETENESS: complete on the 3' end.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_065683.2 CDS 284..2806 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_020632.2 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant 1, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK 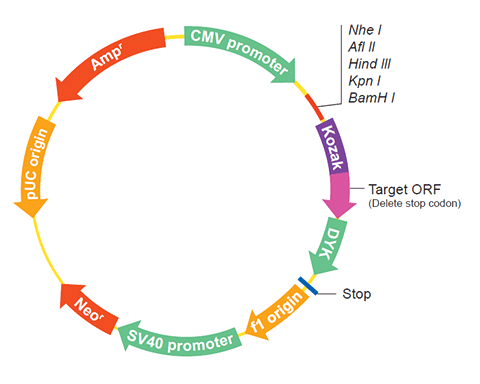 NM_020632.2
NM_020632.2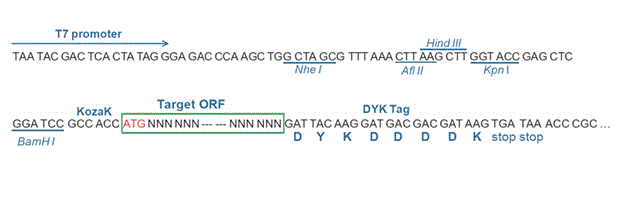
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu15055 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version NM_130841.2 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1570896000000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from DA857655.1, BC109305.1, AF245517.1 and BC109304.1. On Jan 19, 2006 this sequence version replaced NM_130841.1. Transcript Variant: This variant (3) differs in the 5' UTR compared to variant 1. Variants 1, 2, and 3 encode the same protein. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## CDS exon combination :: AF245517.1, AK292945.1 [ECO:0000331] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1968832, SAMEA1968968 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## COMPLETENESS: complete on the 3' end.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_570856.2 CDS 239..2761 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_130841.2 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant 3, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  NM_130841.2
NM_130841.2
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu15055 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version NM_020632.3 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1570896000000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from DB230144.1, BC109305.1, AF245517.1 and BC109304.1. This sequence is a reference standard in the RefSeqGene project. On Nov 23, 2018 this sequence version replaced NM_020632.2. Transcript Variant: This variant (1) is the longest transcript. Variants 1, 2, and 3 encode the same protein. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: AK292945.1, AF245517.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1968832, SAMEA1968968 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## ##RefSeq-Attributes-START## MANE Ensembl match :: ENST00000310018.7/ ENSP00000308122.2 RefSeq Select criteria :: based on conservation, expression, longest protein ##RefSeq-Attributes-END## COMPLETENESS: full length.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_065683.2 CDS 284..2806 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_020632.3 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant 1, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  NM_020632.3
NM_020632.3
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu15055 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version NM_130840.3 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1570896000000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from DB230144.1, BC109305.1, AF245517.1 and BC109304.1. On May 31, 2019 this sequence version replaced NM_130840.2. Transcript Variant: This variant (2) lacks an exon in the 5' UTR compared to variant 1. Variants 1, 2, and 3 encode the same protein. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: BC109304.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1968832, SAMEA1968968 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## COMPLETENESS: complete on the 3' end.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_570855.2 CDS 181..2703 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_130840.3 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant 2, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  NM_130840.3
NM_130840.3
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu15055 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version NM_130840.2 Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1550246400000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform 4 Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from DB230144.1, BC109305.1, AF245517.1 and BC109304.1. On Jan 19, 2006 this sequence version replaced NM_130840.1. Transcript Variant: This variant (2) lacks an exon in the 5' UTR compared to variant 1. Variants 1, 2, and 3 encode the same protein. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: BC109304.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1968832, SAMEA1968968 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## COMPLETENESS: complete on the 3' end.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_570855.2 CDS 181..2703 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_130840.2 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant 2, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  NM_130840.2
NM_130840.2
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu15055 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version XM_005250393.1 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1575475200000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform X1 Comment Comment: MODEL REFSEQ: This record is predicted by automated computational analysis. This record is derived from a genomic sequence (NC_000007.14) annotated using gene prediction method: Gnomon, supported by mRNA and EST evidence. Also see: Documentation of NCBI's Annotation Process ##Genome-Annotation-Data-START## Annotation Provider :: NCBI Annotation Status :: Updated annotation Annotation Name :: Homo sapiens Updated Annotation Release 109.20191205 Annotation Version :: 109.20191205 Annotation Pipeline :: NCBI eukaryotic genome annotation pipeline Annotation Software Version :: 8.3 Annotation Method :: Best-placed RefSeq; propagated RefSeq model Features Annotated :: Gene; mRNA; CDS; ncRNA ##Genome-Annotation-Data-END##
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq XP_005250450.1 CDS 631..3153 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version XM_005250393.1 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant X1, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  XM_005250393.1
XM_005250393.1
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu15055 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_005250393.1 , XM_005250394.3 , NM_130841.2 , NM_020632.3 , NM_020632.2 , NM_130840.3 , NM_130840.2 Accession Version XM_005250394.3 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2523bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1575475200000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product V-type proton ATPase 116 kDa subunit a isoform X1 Comment Comment: MODEL REFSEQ: This record is predicted by automated computational analysis. This record is derived from a genomic sequence (NC_000007.14) annotated using gene prediction method: Gnomon, supported by EST evidence. Also see: Documentation of NCBI's Annotation Process On Jun 6, 2016 this sequence version replaced XM_005250394.2. ##Genome-Annotation-Data-START## Annotation Provider :: NCBI Annotation Status :: Updated annotation Annotation Name :: Homo sapiens Updated Annotation Release 109.20191205 Annotation Version :: 109.20191205 Annotation Pipeline :: NCBI eukaryotic genome annotation pipeline Annotation Software Version :: 8.3 Annotation Method :: Best-placed RefSeq; propagated RefSeq model Features Annotated :: Gene; mRNA; CDS; ncRNA ##Genome-Annotation-Data-END##
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq XP_005250451.1 CDS 543..3065 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version XM_005250394.3 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit a4 (ATP6V0A4), transcript variant X2, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  XM_005250394.3
XM_005250394.3
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521ATGGTGTCTG TGTTTCGAAG CGAGGAGATG TGTTTGTCAC AACTGTTTCT CCAGGTGGAA
GCTGCATATT GCTGTGTGGC TGAGCTCGGA GAGCTCGGAT TGGTTCAGTT CAAAGATTTA
AATATGAATG TGAACAGCTT TCAAAGGAAA TTTGTGAATG AAGTCAGAAG GTGTGAATCA
CTGGAGAGAA TCCTCCGTTT TCTGGAAGAC GAGATGCAAA ATGAGATTGT AGTTCAGTTG
CTCGAGAAAA GCCCACTGAC CCCGCTCCCA CGGGAAATGA TTACCCTGGA GACTGTTCTA
GAAAAACTGG AAGGAGAGTT ACAGGAAGCC AACCAGAACC AGCAGGCCTT GAAACAAAGC
TTCCTAGAAC TGACAGAACT GAAATACCTC CTGAAGAAAA CCCAAGACTT CTTTGAGACG
GAAACCAATT TAGCTGATGA TTTCTTTACT GAGGACACTT CTGGCCTCCT GGAGTTGAAA
GCAGTGCCTG CATATATGAC CGGAAAGTTG GGGTTCATAG CCGGTGTGAT CAACAGGGAG
AGGATGGCTT CCTTTGAGCG GTTACTGTGG CGAATCTGCC GAGGAAACGT GTACTTGAAG
TTCAGTGAGA TGGACGCCCC TCTGGAGGAT CCTGTGACGA AAGAAGAAAT TCAGAAGAAC
ATATTCATCA TATTTTACCA AGGAGAGCAG CTCAGGCAGA AAATCAAGAA GATCTGTGAT
GGGTTTCGAG CCACTGTCTA CCCTTGCCCA GAGCCTGCGG TGGAGCGCAG AGAGATGTTG
GAGAGCGTCA ATGTGAGGCT GGAAGATTTA ATCACCGTCA TAACACAAAC AGAGTCTCAC
CGCCAGCGCC TGCTGCAGGA AGCCGCTGCC AACTGGCACT CCTGGCTCAT CAAGGTGCAG
AAGATGAAAG CTGTCTACCA CATCCTGAAC ATGTGCAACA TCGACGTCAC CCAGCAGTGT
GTCATCGCCG AGATCTGGTT CCCGGTGGCA GATGCCACAC GTATCAAGAG GGCACTGGAG
CAAGGCATGG AACTAAGTGG CTCCTCCATG GCCCCCATCA TGACCACAGT GCAATCTAAA
ACAGCCCCTC CCACATTTAA CAGGACCAAT AAATTCACAG CTGGCTTCCA GAATATTGTT
GATGCCTATG GTGTCGGCAG CTACCGGGAG ATAAACCCAG CCCCCTACAC CATCATCACT
TTCCCCTTCC TGTTCGCTGT GATGTTTGGA GACTGTGGTC ATGGAACCGT GATGCTCCTG
GCTGCACTTT GGATGATTCT GAATGAGAGA CGCTTGCTCT CCCAGAAGAC AGACAATGAG
ATTTGGAACA CCTTCTTCCA CGGGCGCTAT CTGATCCTAC TTATGGGCAT CTTCTCCATC
TACACGGGTT TGATCTACAA TGACTGCTTC TCCAAGTCCT TGAACATCTT TGGCTCTTCT
TGGAGTGTCC AACCCATGTT CAGAAACGGC ACATGGAATA CTCATGTAAT GGAGGAAAGT
CTATATCTGC AGCTGGACCC AGCCATACCA GGAGTGTATT TTGGAAATCC ATACCCGTTT
GGGATTGATC CGATTTGGAA CTTGGCTTCA AACAAACTCA CATTTCTGAA CTCGTATAAA
ATGAAGATGT CGGTGATCCT GGGAATTGTC CAGATGGTTT TCGGTGTCAT CCTCAGCCTT
TTCAATCACA TATACTTCAG AAGAACTCTC AACATCATTC TGCAATTTAT CCCTGAGATG
ATTTTTATCC TGTGTCTGTT TGGATACCTG GTTTTCATGA TCATTTTCAA ATGGTGCTGC
TTTGACGTCC ATGTATCTCA GCACGCCCCC AGCATCCTCA TCCACTTCAT CAACATGTTT
CTGTTTAACT ACAGTGACTC TTCCAACGCA CCCCTCTACA AACATCAGCA AGAAGTCCAA
AGTTTCTTTG TGGTTATGGC TTTGATTTCT GTGCCGTGGA TGCTTCTGAT TAAGCCGTTT
ATTCTTAGAG CCAGTCATCG GAAATCCCAG CTGCAGGCAT CCAGGATCCA AGAAGATGCC
ACTGAGAACA TTGAAGGTGA TAGCTCCAGC CCTTCTAGCC GTTCTGGCCA GAGGACTTCT
GCAGATACCC ACGGGGCTCT GGACGACCAT GGAGAAGAGT TCAACTTTGG AGACGTCTTT
GTCCACCAAG CCATCCACAC CATCGAGTAC TGCCTGGGCT GCATTTCAAA CACAGCCTCC
TACCTGCGGC TCTGGGCCCT CAGCCTGGCT CATGCACAAC TGTCTGAAGT GCTCTGGACT
ATGGTGATGA ACAGCGGCCT TCAGACGCGA GGCTGGGGAG GAATCGTCGG GGTTTTTATT
ATTTTTGCCG TATTTGCTGT CCTGACAGTA GCCATCCTTC TGATCATGGA GGGCCTCTCT
GCTTTCCTGC ACGCCCTGCG ACTGCACTGG GTTGAGTTCC AGAACAAGTT CTATGTCGGG
GATGGTTACA AGTTTTCTCC ATTCTCCTTT AAACACATCC TGGATGGCAC AGCCGAGGAG
TAGThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
-
PubMed
Clinical and genetic analysis of distal renal tubular acidosis in three Chinese children.
Renal failure40(1)520-526(2018 Nov)
Liu J,Shen Q,Li G,Zhai Y,Fang X,Xu H
Five Novel Mutations in Chinese Children with Primary Distal Renal Tubular Acidosis.
Genetic testing and molecular biomarkers22(10)599-606(2018 Oct)
Zhang R,Wang C,Lang Y,Gao Y,Chen Z,Lu J,Zhao X,Shao L
Distal renal tubular acidosis in a Libyan patient: Evidence for digenic inheritance.
European journal of medical genetics61(1)1-7(2018 Jan)
Nagara M,Papagregoriou G,Ben Abdallah R,Landoulsi Z,Bouyacoub Y,Elouej S,Kefi R,Pippucci T,Voskarides K,Bashamboo A,McElreavey K,Hachicha M,Romeo G,Seri M,Deltas C,Abdelhak S
The genetic and clinical spectrum of a large cohort of patients with distal renal tubular acidosis.
Kidney international91(5)1243-1255(2017 05)
Palazzo V,Provenzano A,Becherucci F,Sansavini G,Mazzinghi B,Orlandini V,Giunti L,Roperto RM,Pantaleo M,Artuso R,Andreucci E,Bargiacchi S,Traficante G,Stagi S,Murer L,Benetti E,Emma F,Giordano M,Rivieri F,Colussi G,Penco S,Manfredini E,Caruso MR,Garavelli L,Andrulli S,Vergine G,Miglietti N,Mancini E,Malaventura C,Percesepe A,Grosso E,Materassi M,Romagnani P,Giglio S
-
-
Most Popular Services
-
Services & Products
-
News & Blogs
- Scientists show how diet reverses diabetes
- Tackling Tumor Relapse with More Sensitive Engineered T Cells
- Jay Keasling- Synthetic Biology Solutions for Future Problems
- Keeping your age a secret? Bacteria can tell the truth!
- Uncovering Immunogenic Peptides of Clinical Significance in CRISPR/Cas9
- GenScript joins the HIV Vaccine Development
- The cause of heart disease is linked to a specific type of foreign lipid
- Scientists developed an innovative, label-free approach for visualizing whole-brain changes in Alzheimer’s disease
-
-
-
PubMed
 Hi!Ask me about GenScript services and products! I can answer questions or connect you to a live person.
Hi!Ask me about GenScript services and products! I can answer questions or connect you to a live person. -





































