| Gene Symbol | EPHB4 |
| Entrez Gene ID | 2050 |
| Full Name | EPH receptor B4 |
| Synonyms | HFASD,HTK,MYK1,TYRO11 |
| General protein information |
|
| Gene Type | protein-coding |
| Organism | Homo sapiens(human) |
| Genome | |
| Summary | Ephrin receptors and their ligands, the ephrins, mediate numerous developmental processes, particularly in the nervous system. Based on their structures and sequence relationships, ephrins are divided into the ephrin-A (EFNA) class, which are anchored to the membrane by a glycosylphosphatidylinositol linkage, and the ephrin-B (EFNB) class, which are transmembrane proteins. The Eph family of receptors are divided into 2 groups based on the similarity of their extracellular domain sequences and their affinities for binding ephrin-A and ephrin-B ligands. Ephrin receptors make up the largest subgroup of the receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family. The protein encoded by this gene binds to ephrin-B2 and plays an essential role in vascular development. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]. |
| Disorder MIM: | |
| Disorder Html: | {Hydrops fetalis, nonimmune, and/or atrial septal defect}, 617300 (3) |
-
REAGENT SERVICES
Hot!
-
Most Popular Services
-
Molecular Biology
-
Recombinant Antibody/Protein
-
Reagent Antibody
-
CRISPR Gene Editing
-
DNA Mutant Library
-
IVT RNA and LNP Formulations
-
Oligo Synthesis
-
Peptides
-
Cell Engineering
-
- Gene Synthesis FLASH Gene
- GenBrick™ Up to 200kb
- Gene Fragments Up to 3kb now
- Plasmid DNA Preparation Upgraded
- Cloning and Subcloning
- ORF cDNA Clones
- mRNA Plasmid Solutions New!
- Cell free mRNA Template New!
- AAV Plasmid Solutions New!
- Mutagenesis
- GenCircle™ Double-Stranded DNA New!
- GenSmart™ Online Tools
-
-
PRODUCTS
-
Most Popular Reagents
-
 Instruments
Instruments
-
Antibodies
-
ELISA Kits
-
Protein Electrophoresis and Blotting
-
Protein and Antibody Purification
-
Recombinant Proteins
-
Molecular Biology
-
Stable Cell Lines
-
Cell Isolation and Activation
-
 IVD Raw Materials
IVD Raw Materials
-
 Therapy Applications
Therapy Applications
-
Resources
-
- All Instruments
- Automated Protein and Antibody Purification SystemNew!
- Automated Plasmid MaxiprepHot!
- Automated Plasmid/Protein/Antibody Mini-scale Purification
- eBlot™ Protein Transfer System
- eStain™ Protein Staining System
- eZwest™ Lite Automated Western Blotting Device
- CytoSinct™ 1000 Cell Isolation Instrument
-
- Pharmacokinetics and Immunogenicity ELISA Kits
- Viral Titration QC ELISA Kits
- -- Lentivirus Titer p24 ELISA KitHot!
- -- MuLV Titer p30 ELISA KitNew!
- -- AAV2 and AAVX Titer Capsid ELISA Kits
- Residual Detection ELISA Kits
- -- T7 RNA Polymerase ELISA KitNew!
- -- BSA ELISA Kit, 2G
- -- Cas9 ELISA KitHot!
- -- Protein A ELISA KitHot!
- -- His tagged protein detection & purification
- dsRNA ELISA Kit
- Endonuclease ELISA Kit
- COVID-19 Detection cPass™ Technology Kits
-
- Automated Maxi-Plasmid PurificationHot!
- Automated Mini-Plasmid PurificationNew!
- PCR Reagents
- S.marcescens Nuclease Benz-Neburase™
- DNA Assembly GenBuilder™
- Cas9 / Cas12a / Cas13a Nucleases
- Base and Prime Editing Nucleases
- GMP Cas9 Nucleases
- CRISPR sgRNA Synthesis
- HDR Knock-in Template
- CRISPR Gene Editing Kits and Antibodies
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Anti-Camelid VHH]() MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
-
![ELISA Kits]() ELISA Kits
ELISA Kits
-
![Precast Gels]() SurePAGE™ Precast Gels
SurePAGE™ Precast Gels
-
![Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System]() AmMag™ Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System
AmMag™ Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System
-
![Target Proteins]() Target Proteins
Target Proteins
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Stable Cell Lines]() Stable Cell Lines
Stable Cell Lines
-
![Cell Isolation and Activation]() Cell Isolation and Activation
Cell Isolation and Activation
-
 IVD Raw Materials
IVD Raw Materials
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
- APPLICATIONS
- RESOURCES
- ABOUT US
- SIGN IN My Account SIGN OUT
- REGISTER
ORF » Species Summary » Homo sapiens » EPHB4 cDNA ORF clone
EPHB4 cDNA ORF clone, Homo sapiens(human)
-
Gene
-
Clones
gRNAs
-
Summary
-
mRNA and Protein(s)
mRNA Protein Name XM_017011816.1 XP_016867305.1 ephrin type-B receptor 4 isoform X1 NM_004444.4 NP_004435.3 ephrin type-B receptor 4 precursor NM_004444.5 NP_004435.3 ephrin type-B receptor 4 precursor -
Pathways from BioSystems

-
Homologies
Homo sapiens (human) EPHB4 NP_004435.3 Canis lupus familiaris (dog) EPHB4 XP_546948.3 Mus musculus (house mouse) Ephb4 NP_001153043.1 Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) Ephb4 XP_003751205.1 Macaca mulatta (Rhesus monkey) EPHB4 XP_002803271.1 Bos taurus (cattle) EPHB4 NP_001193197.1 Danio rerio (zebrafish) ephb4b NP_571492.1 Pan troglodytes (chimpanzee) EPHB4 XP_519269.3 Danio rerio (zebrafish) ephb4a NP_571489.1 -
Gene Ontology

-
Bibliography
Related articles in PubMed
Mutations in Chromatin Modifier and Ephrin Signaling Genes in Vein of Galen Malformation.
Duran D, Zeng X, Jin SC, Choi J, Nelson-Williams C, Yatsula B, Gaillard J, Furey CG, Lu Q, Timberlake AT, Dong W, Sorscher MA, Loring E, Klein J, Allocco A, Hunt A, Conine S, Karimy JK, Youngblood MW, Zhang J, DiLuna ML, Matouk CC, Mane S, Tikhonova IR, Castaldi C, López-Giráldez F, Knight J, Haider S, Soban M, Alper SL, Komiyama M, Ducruet AF, Zabramski JM, Dardik A, Walcott BP, Stapleton CJ, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Rodesch G, Jackson E, Smith ER, Orbach DB, Berenstein A, Bilguvar K, Vikkula M, Gunel M, Lifton RP, Kahle KT
Neuron101(3)429-443.e4(2019 02)MicroRNA-454 is involved in regulating trophoblast cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion in preeclampsia by modulating the expression of ephrin receptor B4.
Wang F, Yan J
Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie107746-753(2018 Nov)Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is an essential mediator in drug-resistance of acute myeloid leukemia cells to Adriamycin.
Fu Y, Gao X, Yu X, Liu X, Du Q
Journal of experimental therapeutics & oncology12(4)249-259(2018 Nov)EphB4 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic therapy in experimental glioma.
Uhl C, Markel M, Broggini T, Nieminen M, Kremenetskaia I, Vajkoczy P, Czabanka M
Angiogenesis21(4)873-881(2018 11)Pathogenic variant in EPHB4 results in central conducting lymphatic anomaly.
Li D, Wenger TL, Seiler C, March ME, Gutierrez-Uzquiza A, Kao C, Bhoj E, Tian L, Rosenbach M, Liu Y, Robinson N, Behr M, Chiavacci R, Hou C, Wang T, Bakay M, Pellegrino da Silva R, Perkins JA, Sleiman P, Levine MA, Hicks PJ, Itkin M, Dori Y, Hakonarson H
Human molecular genetics27(18)3233-3245(2018 09)GeneRIFs: Gene References Into Functions What's a GeneRIF?
The following EPHB4 gene cDNA ORF clone sequences were retrieved from the NCBI Reference Sequence Database (RefSeq). These sequences represent the protein coding region of the EPHB4 cDNA ORF which is encoded by the open reading frame (ORF) sequence. ORF sequences can be delivered in our standard vector, pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK or the vector of your choice as an expression/transfection-ready ORF clone. Not the clone you want? Click here to find your clone.

Online Only Promotion
Up to 50% OFF! Starting
from $49/clone-
Reference Sequences (Refseq)
CloneID OHu97077 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) XM_017011816.1 Accession Version XM_017011816.1 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 3018bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1575475200000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product ephrin type-B receptor 4 isoform X1 Comment Comment: MODEL REFSEQ: This record is predicted by automated computational analysis. This record is derived from a genomic sequence (NC_000007.14) annotated using gene prediction method: Gnomon, supported by EST evidence. Also see: Documentation of NCBI's Annotation Process ##Genome-Annotation-Data-START## Annotation Provider :: NCBI Annotation Status :: Updated annotation Annotation Name :: Homo sapiens Updated Annotation Release 109.20191205 Annotation Version :: 109.20191205 Annotation Pipeline :: NCBI eukaryotic genome annotation pipeline Annotation Software Version :: 8.3 Annotation Method :: Best-placed RefSeq; propagated RefSeq model Features Annotated :: Gene; mRNA; CDS; ncRNA ##Genome-Annotation-Data-END##
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521
2581
2641
2701
2761
2821
2881
2941
3001ATGGAGCTCC GGGTGCTGCT CTGCTGGGCT TCGTTGGCCG CAGCTTTGGA AGAGACCCTG
CTGAACACAA AATTGGAAAC TGCTGATCTG AAGTGGGTGA CATTCCCTCA GGTGGACGGG
CAGTGGGAGG AACTGAGCGG CCTGGATGAG GAACAGCACA GCGTGCGCAC CTACGAAGTG
TGTGACGTGC AGCGTGCCCC GGGCCAGGCC CACTGGCTTC GCACAGGTTG GGTCCCACGG
CGGGGCGCCG TCCACGTGTA CGCCACGCTG CGCTTCACCA TGCTCGAGTG CCTGTCCCTG
CCTCGGGCTG GGCGCTCCTG CAAGGAGACC TTCACCGTCT TCTACTATGA GAGCGATGCG
GACACGGCCA CGGCCCTCAC GCCAGCCTGG ATGGAGAACC CCTACATCAA GGTGGACACG
GTGGCCGCGG AGCATCTCAC CCGGAAGCGC CCTGGGGCCG AGGCCACCGG GAAGGTGAAT
GTCAAGACGC TGCGTCTGGG ACCGCTCAGC AAGGCTGGCT TCTACCTGGC CTTCCAGGAC
CAGGGTGCCT GCATGGCCCT GCTATCCCTG CACCTCTTCT ACAAAAAGTG CGCCCAGCTG
ACTGTGAACC TGACTCGATT CCCGGAGACT GTGCCTCGGG AGCTGGTTGT GCCCGTGGCC
GGTAGCTGCG TGGTGGATGC CGTCCCCGCC CCTGGCCCCA GCCCCAGCCT CTACTGCCGT
GAGGATGGCC AGTGGGCCGA ACAGCCGGTC ACGGGCTGCA GCTGTGCTCC GGGGTTCGAG
GCAGCTGAGG GGAACACCAA GTGCCGAGCC TGTGCCCAGG GCACCTTCAA GCCCCTGTCA
GGAGAAGGGT CCTGCCAGCC ATGCCCAGCC AATAGCCACT CTAACACCAT TGGATCAGCC
GTCTGCCAGT GCCGCGTCGG GTACTTCCGG GCACGCACAG ACCCCCGGGG TGCACCCTGC
ACCACCCCTC CTTCGGCTCC GCGGAGCGTG GTTTCCCGCC TGAACGGCTC CTCCCTGCAC
CTGGAATGGA GTGCCCCCCT GGAGTCTGGT GGCCGAGAGG ACCTCACCTA CGCCCTCCGC
TGCCGGGAGT GCCGACCCGG AGGCTCCTGT GCGCCCTGCG GGGGAGACCT GACTTTTGAC
CCCGGCCCCC GGGACCTGGT GGAGCCCTGG GTGGTGGTTC GAGGGCTACG TCCTGACTTC
ACCTATACCT TTGAGGTCAC TGCATTGAAC GGGGTATCCT CCTTAGCCAC GGGGCCCGTC
CCATTTGAGC CTGTCAATGT CACCACTGAC CGAGAGGTTA AGGGACAGAG CTACCATGCA
CAAGGGTTCC CTGTGTCTCT GCCTCTCACA GTACCTCCTG CAGTGTCTGA CATCCGGGTG
ACGCGGTCCT CACCCAGCAG CTTGAGCCTG GCCTGGGCTG TTCCCCGGGC ACCCAGTGGG
GCTGTGCTGG ACTACGAGGT CAAATACCAT GAGAAGGGCG CCGAGGGTCC CAGCAGCGTG
CGGTTCCTGA AGACGTCAGA AAACCGGGCA GAGCTGCGGG GGCTGAAGCG GGGAGCCAGC
TACCTGGTGC AGGTACGGGC GCGCTCTGAG GCCGGCTACG GGCCCTTCGG CCAGGAACAT
CACAGCCAGA CCCAACTGGA TGAGAGCGAG GGCTGGCGGG AGCAGCTGGC CCTGATTGCG
GGCACGGCAG TCGTGGGTGT GGTCCTGGTC CTGGTGGTCA TTGTGGTCGC AGTTCTCTGC
CTCAGGAAGC AGAGCAATGG GAGAGAAGCA GAATATTCGG ACAAACACGG ACAGTATCTC
ATCGGACATG GTACTAAGGT CTACATCGAC CCCTTCACTT ATGAAGACCC TAATGAGGCT
GTGAGGGAAT TTGCAAAAGA GATCGATGTC TCCTACGTCA AGATTGAAGA GGTGATTGGT
GCAGGTGAGT TTGGCGAGGT GTGCCGGGGG CGGCTCAAGG CCCCAGGGAA GAAGGAGAGC
TGTGTGGCAA TCAAGACCCT GAAGGGTGGC TACACGGAGC GGCAGCGGCG TGAGTTTCTG
AGCGAGGCCT CCATCATGGG CCAGTTCGAG CACCCCAATA TCATCCGCCT GGAGGGCGTG
GTCACCAACA GCATGCCCGT CATGATTCTC ACAGAGTTCA TGGAGAACGG CGCCCTGGAC
TCCTTCCTGC GGCTAAACGA CGGACAGTTC ACAGTCATCC AGCTCGTGGG CATGCTGCGG
GGCATCGCCT CGGGCATGCG GTACCTTGCC GAGATGAGCT ACGTCCACCG AGACCTGGCT
GCTCGCAACA TCCTAGTCAA CAGCAACCTC GTCTGCAAAG TGTCTGACTT TGGCCTTTCC
CGATTCCTGG AGGAGAACTC TTCCGATCCC ACCTACACGA GCTCCCTGGG AGGAAAGATT
CCCATCCGAT GGACTGCCCC GGAGGCCATT GCCTTCCGGA AGTTCACTTC CGCCAGTGAT
GCCTGGAGTT ACGGGATTGT GATGTGGGAG GTGATGTCAT TTGGGGAGAG GCCGTACTGG
GACATGAGCA ATCAGGACGT GATCAATGCC ATTGAACAGG ACTACCGGCT GCCCCCGCCC
CCAGACTGTC CCACCTCCCT CCACCAGCTC ATGCTGGACT GTTGGCAGAA AGACCGGAAT
GCCCGGCCCC GCTTCCCCCA GGTGGTCAGC GCCCTGGACA AGATGATCCG GAACCCCGCC
AGCCTCAAAA TCGTGGCCCG GGAGAATGGC GGGGCCTCAC ACCCTCTCCT GGACCAGCGG
CAGCCTCACT ACTCAGCTTT TGGCTCTGTG GGCGAGTGGC TTCGGGCCAT CAAAATGGGA
AGATACGAAG AAAGTTTCGC AGCCGCTGGC TTTGGCTCCT TCGAGCTGGT CAGCCAGATC
TCTGCTGAGG ACCTGCTCCG AATCGGAGTC ACTCTGGCGG GACACCAGAA GAAAATCTTG
GCCAGTGTCC AGCACATGAA GTCCCAGGCC AAGCCGGGAA CCCCGGGTGG GACAGGAGGA
CCGGCCCCGC AGTACTGAThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq XP_016867305.1 CDS 95..3112 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version XM_017011816.1 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens EPH receptor B4 (EPHB4), transcript variant X1, mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK 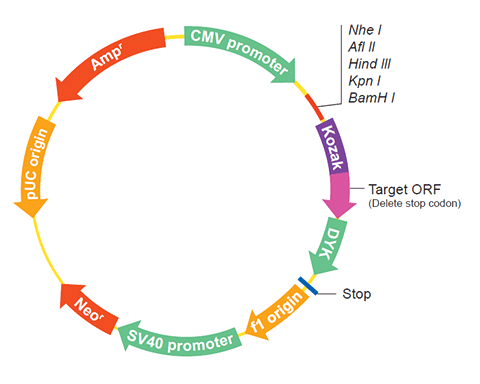 XM_017011816.1
XM_017011816.1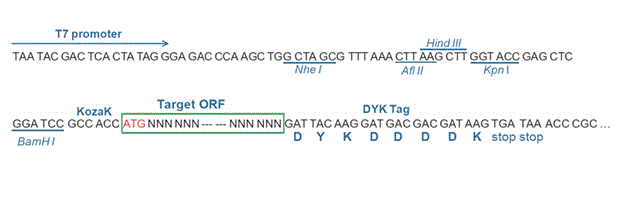
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521
2581
2641
2701
2761
2821
2881
2941
3001ATGGAGCTCC GGGTGCTGCT CTGCTGGGCT TCGTTGGCCG CAGCTTTGGA AGAGACCCTG
CTGAACACAA AATTGGAAAC TGCTGATCTG AAGTGGGTGA CATTCCCTCA GGTGGACGGG
CAGTGGGAGG AACTGAGCGG CCTGGATGAG GAACAGCACA GCGTGCGCAC CTACGAAGTG
TGTGACGTGC AGCGTGCCCC GGGCCAGGCC CACTGGCTTC GCACAGGTTG GGTCCCACGG
CGGGGCGCCG TCCACGTGTA CGCCACGCTG CGCTTCACCA TGCTCGAGTG CCTGTCCCTG
CCTCGGGCTG GGCGCTCCTG CAAGGAGACC TTCACCGTCT TCTACTATGA GAGCGATGCG
GACACGGCCA CGGCCCTCAC GCCAGCCTGG ATGGAGAACC CCTACATCAA GGTGGACACG
GTGGCCGCGG AGCATCTCAC CCGGAAGCGC CCTGGGGCCG AGGCCACCGG GAAGGTGAAT
GTCAAGACGC TGCGTCTGGG ACCGCTCAGC AAGGCTGGCT TCTACCTGGC CTTCCAGGAC
CAGGGTGCCT GCATGGCCCT GCTATCCCTG CACCTCTTCT ACAAAAAGTG CGCCCAGCTG
ACTGTGAACC TGACTCGATT CCCGGAGACT GTGCCTCGGG AGCTGGTTGT GCCCGTGGCC
GGTAGCTGCG TGGTGGATGC CGTCCCCGCC CCTGGCCCCA GCCCCAGCCT CTACTGCCGT
GAGGATGGCC AGTGGGCCGA ACAGCCGGTC ACGGGCTGCA GCTGTGCTCC GGGGTTCGAG
GCAGCTGAGG GGAACACCAA GTGCCGAGCC TGTGCCCAGG GCACCTTCAA GCCCCTGTCA
GGAGAAGGGT CCTGCCAGCC ATGCCCAGCC AATAGCCACT CTAACACCAT TGGATCAGCC
GTCTGCCAGT GCCGCGTCGG GTACTTCCGG GCACGCACAG ACCCCCGGGG TGCACCCTGC
ACCACCCCTC CTTCGGCTCC GCGGAGCGTG GTTTCCCGCC TGAACGGCTC CTCCCTGCAC
CTGGAATGGA GTGCCCCCCT GGAGTCTGGT GGCCGAGAGG ACCTCACCTA CGCCCTCCGC
TGCCGGGAGT GCCGACCCGG AGGCTCCTGT GCGCCCTGCG GGGGAGACCT GACTTTTGAC
CCCGGCCCCC GGGACCTGGT GGAGCCCTGG GTGGTGGTTC GAGGGCTACG TCCTGACTTC
ACCTATACCT TTGAGGTCAC TGCATTGAAC GGGGTATCCT CCTTAGCCAC GGGGCCCGTC
CCATTTGAGC CTGTCAATGT CACCACTGAC CGAGAGGTTA AGGGACAGAG CTACCATGCA
CAAGGGTTCC CTGTGTCTCT GCCTCTCACA GTACCTCCTG CAGTGTCTGA CATCCGGGTG
ACGCGGTCCT CACCCAGCAG CTTGAGCCTG GCCTGGGCTG TTCCCCGGGC ACCCAGTGGG
GCTGTGCTGG ACTACGAGGT CAAATACCAT GAGAAGGGCG CCGAGGGTCC CAGCAGCGTG
CGGTTCCTGA AGACGTCAGA AAACCGGGCA GAGCTGCGGG GGCTGAAGCG GGGAGCCAGC
TACCTGGTGC AGGTACGGGC GCGCTCTGAG GCCGGCTACG GGCCCTTCGG CCAGGAACAT
CACAGCCAGA CCCAACTGGA TGAGAGCGAG GGCTGGCGGG AGCAGCTGGC CCTGATTGCG
GGCACGGCAG TCGTGGGTGT GGTCCTGGTC CTGGTGGTCA TTGTGGTCGC AGTTCTCTGC
CTCAGGAAGC AGAGCAATGG GAGAGAAGCA GAATATTCGG ACAAACACGG ACAGTATCTC
ATCGGACATG GTACTAAGGT CTACATCGAC CCCTTCACTT ATGAAGACCC TAATGAGGCT
GTGAGGGAAT TTGCAAAAGA GATCGATGTC TCCTACGTCA AGATTGAAGA GGTGATTGGT
GCAGGTGAGT TTGGCGAGGT GTGCCGGGGG CGGCTCAAGG CCCCAGGGAA GAAGGAGAGC
TGTGTGGCAA TCAAGACCCT GAAGGGTGGC TACACGGAGC GGCAGCGGCG TGAGTTTCTG
AGCGAGGCCT CCATCATGGG CCAGTTCGAG CACCCCAATA TCATCCGCCT GGAGGGCGTG
GTCACCAACA GCATGCCCGT CATGATTCTC ACAGAGTTCA TGGAGAACGG CGCCCTGGAC
TCCTTCCTGC GGCTAAACGA CGGACAGTTC ACAGTCATCC AGCTCGTGGG CATGCTGCGG
GGCATCGCCT CGGGCATGCG GTACCTTGCC GAGATGAGCT ACGTCCACCG AGACCTGGCT
GCTCGCAACA TCCTAGTCAA CAGCAACCTC GTCTGCAAAG TGTCTGACTT TGGCCTTTCC
CGATTCCTGG AGGAGAACTC TTCCGATCCC ACCTACACGA GCTCCCTGGG AGGAAAGATT
CCCATCCGAT GGACTGCCCC GGAGGCCATT GCCTTCCGGA AGTTCACTTC CGCCAGTGAT
GCCTGGAGTT ACGGGATTGT GATGTGGGAG GTGATGTCAT TTGGGGAGAG GCCGTACTGG
GACATGAGCA ATCAGGACGT GATCAATGCC ATTGAACAGG ACTACCGGCT GCCCCCGCCC
CCAGACTGTC CCACCTCCCT CCACCAGCTC ATGCTGGACT GTTGGCAGAA AGACCGGAAT
GCCCGGCCCC GCTTCCCCCA GGTGGTCAGC GCCCTGGACA AGATGATCCG GAACCCCGCC
AGCCTCAAAA TCGTGGCCCG GGAGAATGGC GGGGCCTCAC ACCCTCTCCT GGACCAGCGG
CAGCCTCACT ACTCAGCTTT TGGCTCTGTG GGCGAGTGGC TTCGGGCCAT CAAAATGGGA
AGATACGAAG AAAGTTTCGC AGCCGCTGGC TTTGGCTCCT TCGAGCTGGT CAGCCAGATC
TCTGCTGAGG ACCTGCTCCG AATCGGAGTC ACTCTGGCGG GACACCAGAA GAAAATCTTG
GCCAGTGTCC AGCACATGAA GTCCCAGGCC AAGCCGGGAA CCCCGGGTGG GACAGGAGGA
CCGGCCCCGC AGTACTGAThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu13402 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) NM_004444.4 , NM_004444.5 Accession Version NM_004444.4 Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2964bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1514390400000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product ephrin type-B receptor 4 precursor Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from CB962032.1, BC052804.1 and AY056048.1. This sequence is a reference standard in the RefSeqGene project. On Nov 16, 2004 this sequence version replaced NM_004444.3. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: BC052804.1, U07695.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1965299, SAMEA1966682 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## COMPLETENESS: complete on the 3' end.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521
2581
2641
2701
2761
2821
2881
2941ATGGAGCTCC GGGTGCTGCT CTGCTGGGCT TCGTTGGCCG CAGCTTTGGA AGAGACCCTG
CTGAACACAA AATTGGAAAC TGCTGATCTG AAGTGGGTGA CATTCCCTCA GGTGGACGGG
CAGTGGGAGG AACTGAGCGG CCTGGATGAG GAACAGCACA GCGTGCGCAC CTACGAAGTG
TGTGACGTGC AGCGTGCCCC GGGCCAGGCC CACTGGCTTC GCACAGGTTG GGTCCCACGG
CGGGGCGCCG TCCACGTGTA CGCCACGCTG CGCTTCACCA TGCTCGAGTG CCTGTCCCTG
CCTCGGGCTG GGCGCTCCTG CAAGGAGACC TTCACCGTCT TCTACTATGA GAGCGATGCG
GACACGGCCA CGGCCCTCAC GCCAGCCTGG ATGGAGAACC CCTACATCAA GGTGGACACG
GTGGCCGCGG AGCATCTCAC CCGGAAGCGC CCTGGGGCCG AGGCCACCGG GAAGGTGAAT
GTCAAGACGC TGCGTCTGGG ACCGCTCAGC AAGGCTGGCT TCTACCTGGC CTTCCAGGAC
CAGGGTGCCT GCATGGCCCT GCTATCCCTG CACCTCTTCT ACAAAAAGTG CGCCCAGCTG
ACTGTGAACC TGACTCGATT CCCGGAGACT GTGCCTCGGG AGCTGGTTGT GCCCGTGGCC
GGTAGCTGCG TGGTGGATGC CGTCCCCGCC CCTGGCCCCA GCCCCAGCCT CTACTGCCGT
GAGGATGGCC AGTGGGCCGA ACAGCCGGTC ACGGGCTGCA GCTGTGCTCC GGGGTTCGAG
GCAGCTGAGG GGAACACCAA GTGCCGAGCC TGTGCCCAGG GCACCTTCAA GCCCCTGTCA
GGAGAAGGGT CCTGCCAGCC ATGCCCAGCC AATAGCCACT CTAACACCAT TGGATCAGCC
GTCTGCCAGT GCCGCGTCGG GTACTTCCGG GCACGCACAG ACCCCCGGGG TGCACCCTGC
ACCACCCCTC CTTCGGCTCC GCGGAGCGTG GTTTCCCGCC TGAACGGCTC CTCCCTGCAC
CTGGAATGGA GTGCCCCCCT GGAGTCTGGT GGCCGAGAGG ACCTCACCTA CGCCCTCCGC
TGCCGGGAGT GCCGACCCGG AGGCTCCTGT GCGCCCTGCG GGGGAGACCT GACTTTTGAC
CCCGGCCCCC GGGACCTGGT GGAGCCCTGG GTGGTGGTTC GAGGGCTACG TCCTGACTTC
ACCTATACCT TTGAGGTCAC TGCATTGAAC GGGGTATCCT CCTTAGCCAC GGGGCCCGTC
CCATTTGAGC CTGTCAATGT CACCACTGAC CGAGAGGTAC CTCCTGCAGT GTCTGACATC
CGGGTGACGC GGTCCTCACC CAGCAGCTTG AGCCTGGCCT GGGCTGTTCC CCGGGCACCC
AGTGGGGCTG TGCTGGACTA CGAGGTCAAA TACCATGAGA AGGGCGCCGA GGGTCCCAGC
AGCGTGCGGT TCCTGAAGAC GTCAGAAAAC CGGGCAGAGC TGCGGGGGCT GAAGCGGGGA
GCCAGCTACC TGGTGCAGGT ACGGGCGCGC TCTGAGGCCG GCTACGGGCC CTTCGGCCAG
GAACATCACA GCCAGACCCA ACTGGATGAG AGCGAGGGCT GGCGGGAGCA GCTGGCCCTG
ATTGCGGGCA CGGCAGTCGT GGGTGTGGTC CTGGTCCTGG TGGTCATTGT GGTCGCAGTT
CTCTGCCTCA GGAAGCAGAG CAATGGGAGA GAAGCAGAAT ATTCGGACAA ACACGGACAG
TATCTCATCG GACATGGTAC TAAGGTCTAC ATCGACCCCT TCACTTATGA AGACCCTAAT
GAGGCTGTGA GGGAATTTGC AAAAGAGATC GATGTCTCCT ACGTCAAGAT TGAAGAGGTG
ATTGGTGCAG GTGAGTTTGG CGAGGTGTGC CGGGGGCGGC TCAAGGCCCC AGGGAAGAAG
GAGAGCTGTG TGGCAATCAA GACCCTGAAG GGTGGCTACA CGGAGCGGCA GCGGCGTGAG
TTTCTGAGCG AGGCCTCCAT CATGGGCCAG TTCGAGCACC CCAATATCAT CCGCCTGGAG
GGCGTGGTCA CCAACAGCAT GCCCGTCATG ATTCTCACAG AGTTCATGGA GAACGGCGCC
CTGGACTCCT TCCTGCGGCT AAACGACGGA CAGTTCACAG TCATCCAGCT CGTGGGCATG
CTGCGGGGCA TCGCCTCGGG CATGCGGTAC CTTGCCGAGA TGAGCTACGT CCACCGAGAC
CTGGCTGCTC GCAACATCCT AGTCAACAGC AACCTCGTCT GCAAAGTGTC TGACTTTGGC
CTTTCCCGAT TCCTGGAGGA GAACTCTTCC GATCCCACCT ACACGAGCTC CCTGGGAGGA
AAGATTCCCA TCCGATGGAC TGCCCCGGAG GCCATTGCCT TCCGGAAGTT CACTTCCGCC
AGTGATGCCT GGAGTTACGG GATTGTGATG TGGGAGGTGA TGTCATTTGG GGAGAGGCCG
TACTGGGACA TGAGCAATCA GGACGTGATC AATGCCATTG AACAGGACTA CCGGCTGCCC
CCGCCCCCAG ACTGTCCCAC CTCCCTCCAC CAGCTCATGC TGGACTGTTG GCAGAAAGAC
CGGAATGCCC GGCCCCGCTT CCCCCAGGTG GTCAGCGCCC TGGACAAGAT GATCCGGAAC
CCCGCCAGCC TCAAAATCGT GGCCCGGGAG AATGGCGGGG CCTCACACCC TCTCCTGGAC
CAGCGGCAGC CTCACTACTC AGCTTTTGGC TCTGTGGGCG AGTGGCTTCG GGCCATCAAA
ATGGGAAGAT ACGAAGAAAG TTTCGCAGCC GCTGGCTTTG GCTCCTTCGA GCTGGTCAGC
CAGATCTCTG CTGAGGACCT GCTCCGAATC GGAGTCACTC TGGCGGGACA CCAGAAGAAA
ATCTTGGCCA GTGTCCAGCA CATGAAGTCC CAGGCCAAGC CGGGAACCCC GGGTGGGACA
GGAGGACCGG CCCCGCAGTA CTGAThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_004435.3 CDS 492..3455 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_004444.4 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens EPH receptor B4 (EPHB4), mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  NM_004444.4
NM_004444.4
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521
2581
2641
2701
2761
2821
2881
2941ATGGAGCTCC GGGTGCTGCT CTGCTGGGCT TCGTTGGCCG CAGCTTTGGA AGAGACCCTG
CTGAACACAA AATTGGAAAC TGCTGATCTG AAGTGGGTGA CATTCCCTCA GGTGGACGGG
CAGTGGGAGG AACTGAGCGG CCTGGATGAG GAACAGCACA GCGTGCGCAC CTACGAAGTG
TGTGACGTGC AGCGTGCCCC GGGCCAGGCC CACTGGCTTC GCACAGGTTG GGTCCCACGG
CGGGGCGCCG TCCACGTGTA CGCCACGCTG CGCTTCACCA TGCTCGAGTG CCTGTCCCTG
CCTCGGGCTG GGCGCTCCTG CAAGGAGACC TTCACCGTCT TCTACTATGA GAGCGATGCG
GACACGGCCA CGGCCCTCAC GCCAGCCTGG ATGGAGAACC CCTACATCAA GGTGGACACG
GTGGCCGCGG AGCATCTCAC CCGGAAGCGC CCTGGGGCCG AGGCCACCGG GAAGGTGAAT
GTCAAGACGC TGCGTCTGGG ACCGCTCAGC AAGGCTGGCT TCTACCTGGC CTTCCAGGAC
CAGGGTGCCT GCATGGCCCT GCTATCCCTG CACCTCTTCT ACAAAAAGTG CGCCCAGCTG
ACTGTGAACC TGACTCGATT CCCGGAGACT GTGCCTCGGG AGCTGGTTGT GCCCGTGGCC
GGTAGCTGCG TGGTGGATGC CGTCCCCGCC CCTGGCCCCA GCCCCAGCCT CTACTGCCGT
GAGGATGGCC AGTGGGCCGA ACAGCCGGTC ACGGGCTGCA GCTGTGCTCC GGGGTTCGAG
GCAGCTGAGG GGAACACCAA GTGCCGAGCC TGTGCCCAGG GCACCTTCAA GCCCCTGTCA
GGAGAAGGGT CCTGCCAGCC ATGCCCAGCC AATAGCCACT CTAACACCAT TGGATCAGCC
GTCTGCCAGT GCCGCGTCGG GTACTTCCGG GCACGCACAG ACCCCCGGGG TGCACCCTGC
ACCACCCCTC CTTCGGCTCC GCGGAGCGTG GTTTCCCGCC TGAACGGCTC CTCCCTGCAC
CTGGAATGGA GTGCCCCCCT GGAGTCTGGT GGCCGAGAGG ACCTCACCTA CGCCCTCCGC
TGCCGGGAGT GCCGACCCGG AGGCTCCTGT GCGCCCTGCG GGGGAGACCT GACTTTTGAC
CCCGGCCCCC GGGACCTGGT GGAGCCCTGG GTGGTGGTTC GAGGGCTACG TCCTGACTTC
ACCTATACCT TTGAGGTCAC TGCATTGAAC GGGGTATCCT CCTTAGCCAC GGGGCCCGTC
CCATTTGAGC CTGTCAATGT CACCACTGAC CGAGAGGTAC CTCCTGCAGT GTCTGACATC
CGGGTGACGC GGTCCTCACC CAGCAGCTTG AGCCTGGCCT GGGCTGTTCC CCGGGCACCC
AGTGGGGCTG TGCTGGACTA CGAGGTCAAA TACCATGAGA AGGGCGCCGA GGGTCCCAGC
AGCGTGCGGT TCCTGAAGAC GTCAGAAAAC CGGGCAGAGC TGCGGGGGCT GAAGCGGGGA
GCCAGCTACC TGGTGCAGGT ACGGGCGCGC TCTGAGGCCG GCTACGGGCC CTTCGGCCAG
GAACATCACA GCCAGACCCA ACTGGATGAG AGCGAGGGCT GGCGGGAGCA GCTGGCCCTG
ATTGCGGGCA CGGCAGTCGT GGGTGTGGTC CTGGTCCTGG TGGTCATTGT GGTCGCAGTT
CTCTGCCTCA GGAAGCAGAG CAATGGGAGA GAAGCAGAAT ATTCGGACAA ACACGGACAG
TATCTCATCG GACATGGTAC TAAGGTCTAC ATCGACCCCT TCACTTATGA AGACCCTAAT
GAGGCTGTGA GGGAATTTGC AAAAGAGATC GATGTCTCCT ACGTCAAGAT TGAAGAGGTG
ATTGGTGCAG GTGAGTTTGG CGAGGTGTGC CGGGGGCGGC TCAAGGCCCC AGGGAAGAAG
GAGAGCTGTG TGGCAATCAA GACCCTGAAG GGTGGCTACA CGGAGCGGCA GCGGCGTGAG
TTTCTGAGCG AGGCCTCCAT CATGGGCCAG TTCGAGCACC CCAATATCAT CCGCCTGGAG
GGCGTGGTCA CCAACAGCAT GCCCGTCATG ATTCTCACAG AGTTCATGGA GAACGGCGCC
CTGGACTCCT TCCTGCGGCT AAACGACGGA CAGTTCACAG TCATCCAGCT CGTGGGCATG
CTGCGGGGCA TCGCCTCGGG CATGCGGTAC CTTGCCGAGA TGAGCTACGT CCACCGAGAC
CTGGCTGCTC GCAACATCCT AGTCAACAGC AACCTCGTCT GCAAAGTGTC TGACTTTGGC
CTTTCCCGAT TCCTGGAGGA GAACTCTTCC GATCCCACCT ACACGAGCTC CCTGGGAGGA
AAGATTCCCA TCCGATGGAC TGCCCCGGAG GCCATTGCCT TCCGGAAGTT CACTTCCGCC
AGTGATGCCT GGAGTTACGG GATTGTGATG TGGGAGGTGA TGTCATTTGG GGAGAGGCCG
TACTGGGACA TGAGCAATCA GGACGTGATC AATGCCATTG AACAGGACTA CCGGCTGCCC
CCGCCCCCAG ACTGTCCCAC CTCCCTCCAC CAGCTCATGC TGGACTGTTG GCAGAAAGAC
CGGAATGCCC GGCCCCGCTT CCCCCAGGTG GTCAGCGCCC TGGACAAGAT GATCCGGAAC
CCCGCCAGCC TCAAAATCGT GGCCCGGGAG AATGGCGGGG CCTCACACCC TCTCCTGGAC
CAGCGGCAGC CTCACTACTC AGCTTTTGGC TCTGTGGGCG AGTGGCTTCG GGCCATCAAA
ATGGGAAGAT ACGAAGAAAG TTTCGCAGCC GCTGGCTTTG GCTCCTTCGA GCTGGTCAGC
CAGATCTCTG CTGAGGACCT GCTCCGAATC GGAGTCACTC TGGCGGGACA CCAGAAGAAA
ATCTTGGCCA GTGTCCAGCA CATGAAGTCC CAGGCCAAGC CGGGAACCCC GGGTGGGACA
GGAGGACCGG CCCCGCAGTA CTGAThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
CloneID OHu13402 Clone ID Related Accession (Same CDS sequence) NM_004444.4 , NM_004444.5 Accession Version NM_004444.5 Latest version! Documents for ORF clone product in default vector Sequence Information ORF Nucleotide Sequence (Length: 2964bp)
Protein sequence
SNPVector pcDNA3.1-C-(k)DYK or customized vector  User Manual
User ManualClone information Clone Map  MSDS
MSDSTag on pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK C terminal DYKDDDDK tags ORF Insert Method CloneEZ™ Seamless cloning technology Insert Structure linear Update Date 1573228800000 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Product ephrin type-B receptor 4 precursor Comment Comment: REVIEWED REFSEQ: This record has been curated by NCBI staff. The reference sequence was derived from AC011895.4, CB962032.1, BC052804.1 and AY056048.1. This sequence is a reference standard in the RefSeqGene project. On Nov 23, 2018 this sequence version replaced NM_004444.4. Publication Note: This RefSeq record includes a subset of the publications that are available for this gene. Please see the Gene record to access additional publications. ##Evidence-Data-START## Transcript exon combination :: BC052804.1, U07695.1 [ECO:0000332] RNAseq introns :: mixed/partial sample support SAMEA1965299, SAMEA1966682 [ECO:0000350] ##Evidence-Data-END## ##RefSeq-Attributes-START## MANE Ensembl match :: ENST00000358173.8/ ENSP00000350896.3 RefSeq Select criteria :: based on conservation, expression ##RefSeq-Attributes-END## COMPLETENESS: full length.
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521
2581
2641
2701
2761
2821
2881
2941ATGGAGCTCC GGGTGCTGCT CTGCTGGGCT TCGTTGGCCG CAGCTTTGGA AGAGACCCTG
CTGAACACAA AATTGGAAAC TGCTGATCTG AAGTGGGTGA CATTCCCTCA GGTGGACGGG
CAGTGGGAGG AACTGAGCGG CCTGGATGAG GAACAGCACA GCGTGCGCAC CTACGAAGTG
TGTGACGTGC AGCGTGCCCC GGGCCAGGCC CACTGGCTTC GCACAGGTTG GGTCCCACGG
CGGGGCGCCG TCCACGTGTA CGCCACGCTG CGCTTCACCA TGCTCGAGTG CCTGTCCCTG
CCTCGGGCTG GGCGCTCCTG CAAGGAGACC TTCACCGTCT TCTACTATGA GAGCGATGCG
GACACGGCCA CGGCCCTCAC GCCAGCCTGG ATGGAGAACC CCTACATCAA GGTGGACACG
GTGGCCGCGG AGCATCTCAC CCGGAAGCGC CCTGGGGCCG AGGCCACCGG GAAGGTGAAT
GTCAAGACGC TGCGTCTGGG ACCGCTCAGC AAGGCTGGCT TCTACCTGGC CTTCCAGGAC
CAGGGTGCCT GCATGGCCCT GCTATCCCTG CACCTCTTCT ACAAAAAGTG CGCCCAGCTG
ACTGTGAACC TGACTCGATT CCCGGAGACT GTGCCTCGGG AGCTGGTTGT GCCCGTGGCC
GGTAGCTGCG TGGTGGATGC CGTCCCCGCC CCTGGCCCCA GCCCCAGCCT CTACTGCCGT
GAGGATGGCC AGTGGGCCGA ACAGCCGGTC ACGGGCTGCA GCTGTGCTCC GGGGTTCGAG
GCAGCTGAGG GGAACACCAA GTGCCGAGCC TGTGCCCAGG GCACCTTCAA GCCCCTGTCA
GGAGAAGGGT CCTGCCAGCC ATGCCCAGCC AATAGCCACT CTAACACCAT TGGATCAGCC
GTCTGCCAGT GCCGCGTCGG GTACTTCCGG GCACGCACAG ACCCCCGGGG TGCACCCTGC
ACCACCCCTC CTTCGGCTCC GCGGAGCGTG GTTTCCCGCC TGAACGGCTC CTCCCTGCAC
CTGGAATGGA GTGCCCCCCT GGAGTCTGGT GGCCGAGAGG ACCTCACCTA CGCCCTCCGC
TGCCGGGAGT GCCGACCCGG AGGCTCCTGT GCGCCCTGCG GGGGAGACCT GACTTTTGAC
CCCGGCCCCC GGGACCTGGT GGAGCCCTGG GTGGTGGTTC GAGGGCTACG TCCTGACTTC
ACCTATACCT TTGAGGTCAC TGCATTGAAC GGGGTATCCT CCTTAGCCAC GGGGCCCGTC
CCATTTGAGC CTGTCAATGT CACCACTGAC CGAGAGGTAC CTCCTGCAGT GTCTGACATC
CGGGTGACGC GGTCCTCACC CAGCAGCTTG AGCCTGGCCT GGGCTGTTCC CCGGGCACCC
AGTGGGGCTG TGCTGGACTA CGAGGTCAAA TACCATGAGA AGGGCGCCGA GGGTCCCAGC
AGCGTGCGGT TCCTGAAGAC GTCAGAAAAC CGGGCAGAGC TGCGGGGGCT GAAGCGGGGA
GCCAGCTACC TGGTGCAGGT ACGGGCGCGC TCTGAGGCCG GCTACGGGCC CTTCGGCCAG
GAACATCACA GCCAGACCCA ACTGGATGAG AGCGAGGGCT GGCGGGAGCA GCTGGCCCTG
ATTGCGGGCA CGGCAGTCGT GGGTGTGGTC CTGGTCCTGG TGGTCATTGT GGTCGCAGTT
CTCTGCCTCA GGAAGCAGAG CAATGGGAGA GAAGCAGAAT ATTCGGACAA ACACGGACAG
TATCTCATCG GACATGGTAC TAAGGTCTAC ATCGACCCCT TCACTTATGA AGACCCTAAT
GAGGCTGTGA GGGAATTTGC AAAAGAGATC GATGTCTCCT ACGTCAAGAT TGAAGAGGTG
ATTGGTGCAG GTGAGTTTGG CGAGGTGTGC CGGGGGCGGC TCAAGGCCCC AGGGAAGAAG
GAGAGCTGTG TGGCAATCAA GACCCTGAAG GGTGGCTACA CGGAGCGGCA GCGGCGTGAG
TTTCTGAGCG AGGCCTCCAT CATGGGCCAG TTCGAGCACC CCAATATCAT CCGCCTGGAG
GGCGTGGTCA CCAACAGCAT GCCCGTCATG ATTCTCACAG AGTTCATGGA GAACGGCGCC
CTGGACTCCT TCCTGCGGCT AAACGACGGA CAGTTCACAG TCATCCAGCT CGTGGGCATG
CTGCGGGGCA TCGCCTCGGG CATGCGGTAC CTTGCCGAGA TGAGCTACGT CCACCGAGAC
CTGGCTGCTC GCAACATCCT AGTCAACAGC AACCTCGTCT GCAAAGTGTC TGACTTTGGC
CTTTCCCGAT TCCTGGAGGA GAACTCTTCC GATCCCACCT ACACGAGCTC CCTGGGAGGA
AAGATTCCCA TCCGATGGAC TGCCCCGGAG GCCATTGCCT TCCGGAAGTT CACTTCCGCC
AGTGATGCCT GGAGTTACGG GATTGTGATG TGGGAGGTGA TGTCATTTGG GGAGAGGCCG
TACTGGGACA TGAGCAATCA GGACGTGATC AATGCCATTG AACAGGACTA CCGGCTGCCC
CCGCCCCCAG ACTGTCCCAC CTCCCTCCAC CAGCTCATGC TGGACTGTTG GCAGAAAGAC
CGGAATGCCC GGCCCCGCTT CCCCCAGGTG GTCAGCGCCC TGGACAAGAT GATCCGGAAC
CCCGCCAGCC TCAAAATCGT GGCCCGGGAG AATGGCGGGG CCTCACACCC TCTCCTGGAC
CAGCGGCAGC CTCACTACTC AGCTTTTGGC TCTGTGGGCG AGTGGCTTCG GGCCATCAAA
ATGGGAAGAT ACGAAGAAAG TTTCGCAGCC GCTGGCTTTG GCTCCTTCGA GCTGGTCAGC
CAGATCTCTG CTGAGGACCT GCTCCGAATC GGAGTCACTC TGGCGGGACA CCAGAAGAAA
ATCTTGGCCA GTGTCCAGCA CATGAAGTCC CAGGCCAAGC CGGGAACCCC GGGTGGGACA
GGAGGACCGG CCCCGCAGTA CTGAThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
RefSeq NP_004435.3 CDS 494..3457 Translation 
Target ORF information:
RefSeq Version NM_004444.5 Organism Homo sapiens(human) Definition Homo sapiens EPH receptor B4 (EPHB4), mRNA. Target ORF information:
Epitope DYKDDDDK Bacterial selection AMPR Mammalian selection NeoR Vector pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK  NM_004444.5
NM_004444.5
ORF Insert Sequence:
1
61
121
181
241
301
361
421
481
541
601
661
721
781
841
901
961
1021
1081
1141
1201
1261
1321
1381
1441
1501
1561
1621
1681
1741
1801
1861
1921
1981
2041
2101
2161
2221
2281
2341
2401
2461
2521
2581
2641
2701
2761
2821
2881
2941ATGGAGCTCC GGGTGCTGCT CTGCTGGGCT TCGTTGGCCG CAGCTTTGGA AGAGACCCTG
CTGAACACAA AATTGGAAAC TGCTGATCTG AAGTGGGTGA CATTCCCTCA GGTGGACGGG
CAGTGGGAGG AACTGAGCGG CCTGGATGAG GAACAGCACA GCGTGCGCAC CTACGAAGTG
TGTGACGTGC AGCGTGCCCC GGGCCAGGCC CACTGGCTTC GCACAGGTTG GGTCCCACGG
CGGGGCGCCG TCCACGTGTA CGCCACGCTG CGCTTCACCA TGCTCGAGTG CCTGTCCCTG
CCTCGGGCTG GGCGCTCCTG CAAGGAGACC TTCACCGTCT TCTACTATGA GAGCGATGCG
GACACGGCCA CGGCCCTCAC GCCAGCCTGG ATGGAGAACC CCTACATCAA GGTGGACACG
GTGGCCGCGG AGCATCTCAC CCGGAAGCGC CCTGGGGCCG AGGCCACCGG GAAGGTGAAT
GTCAAGACGC TGCGTCTGGG ACCGCTCAGC AAGGCTGGCT TCTACCTGGC CTTCCAGGAC
CAGGGTGCCT GCATGGCCCT GCTATCCCTG CACCTCTTCT ACAAAAAGTG CGCCCAGCTG
ACTGTGAACC TGACTCGATT CCCGGAGACT GTGCCTCGGG AGCTGGTTGT GCCCGTGGCC
GGTAGCTGCG TGGTGGATGC CGTCCCCGCC CCTGGCCCCA GCCCCAGCCT CTACTGCCGT
GAGGATGGCC AGTGGGCCGA ACAGCCGGTC ACGGGCTGCA GCTGTGCTCC GGGGTTCGAG
GCAGCTGAGG GGAACACCAA GTGCCGAGCC TGTGCCCAGG GCACCTTCAA GCCCCTGTCA
GGAGAAGGGT CCTGCCAGCC ATGCCCAGCC AATAGCCACT CTAACACCAT TGGATCAGCC
GTCTGCCAGT GCCGCGTCGG GTACTTCCGG GCACGCACAG ACCCCCGGGG TGCACCCTGC
ACCACCCCTC CTTCGGCTCC GCGGAGCGTG GTTTCCCGCC TGAACGGCTC CTCCCTGCAC
CTGGAATGGA GTGCCCCCCT GGAGTCTGGT GGCCGAGAGG ACCTCACCTA CGCCCTCCGC
TGCCGGGAGT GCCGACCCGG AGGCTCCTGT GCGCCCTGCG GGGGAGACCT GACTTTTGAC
CCCGGCCCCC GGGACCTGGT GGAGCCCTGG GTGGTGGTTC GAGGGCTACG TCCTGACTTC
ACCTATACCT TTGAGGTCAC TGCATTGAAC GGGGTATCCT CCTTAGCCAC GGGGCCCGTC
CCATTTGAGC CTGTCAATGT CACCACTGAC CGAGAGGTAC CTCCTGCAGT GTCTGACATC
CGGGTGACGC GGTCCTCACC CAGCAGCTTG AGCCTGGCCT GGGCTGTTCC CCGGGCACCC
AGTGGGGCTG TGCTGGACTA CGAGGTCAAA TACCATGAGA AGGGCGCCGA GGGTCCCAGC
AGCGTGCGGT TCCTGAAGAC GTCAGAAAAC CGGGCAGAGC TGCGGGGGCT GAAGCGGGGA
GCCAGCTACC TGGTGCAGGT ACGGGCGCGC TCTGAGGCCG GCTACGGGCC CTTCGGCCAG
GAACATCACA GCCAGACCCA ACTGGATGAG AGCGAGGGCT GGCGGGAGCA GCTGGCCCTG
ATTGCGGGCA CGGCAGTCGT GGGTGTGGTC CTGGTCCTGG TGGTCATTGT GGTCGCAGTT
CTCTGCCTCA GGAAGCAGAG CAATGGGAGA GAAGCAGAAT ATTCGGACAA ACACGGACAG
TATCTCATCG GACATGGTAC TAAGGTCTAC ATCGACCCCT TCACTTATGA AGACCCTAAT
GAGGCTGTGA GGGAATTTGC AAAAGAGATC GATGTCTCCT ACGTCAAGAT TGAAGAGGTG
ATTGGTGCAG GTGAGTTTGG CGAGGTGTGC CGGGGGCGGC TCAAGGCCCC AGGGAAGAAG
GAGAGCTGTG TGGCAATCAA GACCCTGAAG GGTGGCTACA CGGAGCGGCA GCGGCGTGAG
TTTCTGAGCG AGGCCTCCAT CATGGGCCAG TTCGAGCACC CCAATATCAT CCGCCTGGAG
GGCGTGGTCA CCAACAGCAT GCCCGTCATG ATTCTCACAG AGTTCATGGA GAACGGCGCC
CTGGACTCCT TCCTGCGGCT AAACGACGGA CAGTTCACAG TCATCCAGCT CGTGGGCATG
CTGCGGGGCA TCGCCTCGGG CATGCGGTAC CTTGCCGAGA TGAGCTACGT CCACCGAGAC
CTGGCTGCTC GCAACATCCT AGTCAACAGC AACCTCGTCT GCAAAGTGTC TGACTTTGGC
CTTTCCCGAT TCCTGGAGGA GAACTCTTCC GATCCCACCT ACACGAGCTC CCTGGGAGGA
AAGATTCCCA TCCGATGGAC TGCCCCGGAG GCCATTGCCT TCCGGAAGTT CACTTCCGCC
AGTGATGCCT GGAGTTACGG GATTGTGATG TGGGAGGTGA TGTCATTTGG GGAGAGGCCG
TACTGGGACA TGAGCAATCA GGACGTGATC AATGCCATTG AACAGGACTA CCGGCTGCCC
CCGCCCCCAG ACTGTCCCAC CTCCCTCCAC CAGCTCATGC TGGACTGTTG GCAGAAAGAC
CGGAATGCCC GGCCCCGCTT CCCCCAGGTG GTCAGCGCCC TGGACAAGAT GATCCGGAAC
CCCGCCAGCC TCAAAATCGT GGCCCGGGAG AATGGCGGGG CCTCACACCC TCTCCTGGAC
CAGCGGCAGC CTCACTACTC AGCTTTTGGC TCTGTGGGCG AGTGGCTTCG GGCCATCAAA
ATGGGAAGAT ACGAAGAAAG TTTCGCAGCC GCTGGCTTTG GCTCCTTCGA GCTGGTCAGC
CAGATCTCTG CTGAGGACCT GCTCCGAATC GGAGTCACTC TGGCGGGACA CCAGAAGAAA
ATCTTGGCCA GTGTCCAGCA CATGAAGTCC CAGGCCAAGC CGGGAACCCC GGGTGGGACA
GGAGGACCGG CCCCGCAGTA CTGAThe stop codons will be deleted if pcDNA3.1+/C-(K)DYK vector is selected.
-
PubMed
Mutations in Chromatin Modifier and Ephrin Signaling Genes in Vein of Galen Malformation.
Neuron101(3)429-443.e4(2019 02)
Duran D,Zeng X,Jin SC,Choi J,Nelson-Williams C,Yatsula B,Gaillard J,Furey CG,Lu Q,Timberlake AT,Dong W,Sorscher MA,Loring E,Klein J,Allocco A,Hunt A,Conine S,Karimy JK,Youngblood MW,Zhang J,DiLuna ML,Matouk CC,Mane S,Tikhonova IR,Castaldi C,López-Giráldez F,Knight J,Haider S,Soban M,Alper SL,Komiyama M,Ducruet AF,Zabramski JM,Dardik A,Walcott BP,Stapleton CJ,Aagaard-Kienitz B,Rodesch G,Jackson E,Smith ER,Orbach DB,Berenstein A,Bilguvar K,Vikkula M,Gunel M,Lifton RP,Kahle KT
MicroRNA-454 is involved in regulating trophoblast cell proliferation, apoptosis, and invasion in preeclampsia by modulating the expression of ephrin receptor B4.
Biomedicine & pharmacotherapy = Biomedecine & pharmacotherapie107746-753(2018 Nov)
Wang F,Yan J
Ephrin type-B receptor 4 is an essential mediator in drug-resistance of acute myeloid leukemia cells to Adriamycin.
Journal of experimental therapeutics & oncology12(4)249-259(2018 Nov)
Fu Y,Gao X,Yu X,Liu X,Du Q
EphB4 mediates resistance to antiangiogenic therapy in experimental glioma.
Angiogenesis21(4)873-881(2018 11)
Uhl C,Markel M,Broggini T,Nieminen M,Kremenetskaia I,Vajkoczy P,Czabanka M
Pathogenic variant in EPHB4 results in central conducting lymphatic anomaly.
Human molecular genetics27(18)3233-3245(2018 09)
Li D,Wenger TL,Seiler C,March ME,Gutierrez-Uzquiza A,Kao C,Bhoj E,Tian L,Rosenbach M,Liu Y,Robinson N,Behr M,Chiavacci R,Hou C,Wang T,Bakay M,Pellegrino da Silva R,Perkins JA,Sleiman P,Levine MA,Hicks PJ,Itkin M,Dori Y,Hakonarson H
-
-
Most Popular Services
-
Services & Products
-
News & Blogs
- COVID-19 Pathogenesis: Uncovering New Molecular Mechanisms
- New Study Reveals the Secrets Behind the Longevity Proteins
- Discovering Antibodies with Broader Epitope Specificities
- New Solutions Push the Limits of Engineered T Cells in Solid Tumors
- GenScript’s Codon Optimization faciliates new finding in base editor
- Molecular chainsaw massacre of cancer cells
- Evolving CRISPR/Cas Tools through Engineering Strategies
- DNA Microarrays Enable New CRISPR/Cas9-based Peptide Library Display
-
-
-
PubMed
 Hi!Ask me about GenScript services and products! I can answer questions or connect you to a live person.
Hi!Ask me about GenScript services and products! I can answer questions or connect you to a live person. -





































