-
REAGENT SERVICES
Hot!
-
Most Popular Services
-
Molecular Biology
-
Recombinant Antibody/Protein
-
Reagent Antibody
-
CRISPR Gene Editing
-
DNA Mutant Library
-
IVT RNA and LNP Formulations
-
Oligo Synthesis
-
Peptides
-
Cell Engineering
-
- Gene Synthesis FLASH Gene
- GenBrick™ Up to 200kb
- Gene Fragments Up to 3kb now
- Plasmid DNA Preparation Upgraded
- Cloning and Subcloning
- ORF cDNA Clones
- mRNA Plasmid Solutions New!
- Cell free mRNA Template New!
- AAV Plasmid Solutions New!
- Mutagenesis
- GenCircle™ Double-Stranded DNA New!
- GenSmart™ Online Tools
-
-
PRODUCTS
-
Most Popular Reagents
-
 Instruments
Instruments
-
Antibodies
-
ELISA Kits
-
Protein Electrophoresis and Blotting
-
Protein and Antibody Purification
-
Recombinant Proteins
-
Molecular Biology
-
Stable Cell Lines
-
Cell Isolation and Activation
-
 IVD Raw Materials
IVD Raw Materials
-
 Therapy Applications
Therapy Applications
-
Resources
-
- All Instruments
- Automated Protein and Antibody Purification SystemNew!
- Automated Plasmid MaxiprepHot!
- Automated Plasmid/Protein/Antibody Mini-scale Purification
- eBlot™ Protein Transfer System
- eStain™ Protein Staining System
- eZwest™ Lite Automated Western Blotting Device
- CytoSinct™ 1000 Cell Isolation Instrument
-
- Pharmacokinetics and Immunogenicity ELISA Kits
- Viral Titration QC ELISA Kits
- -- Lentivirus Titer p24 ELISA KitHot!
- -- MuLV Titer p30 ELISA KitNew!
- -- AAV2 and AAVX Titer Capsid ELISA Kits
- Residual Detection ELISA Kits
- -- T7 RNA Polymerase ELISA KitNew!
- -- BSA ELISA Kit, 2G
- -- Cas9 ELISA KitHot!
- -- Protein A ELISA KitHot!
- -- His tagged protein detection & purification
- dsRNA ELISA Kit
- Endonuclease ELISA Kit
- COVID-19 Detection cPass™ Technology Kits
-
- Automated Maxi-Plasmid PurificationHot!
- Automated Mini-Plasmid PurificationNew!
- PCR Reagents
- S.marcescens Nuclease Benz-Neburase™
- DNA Assembly GenBuilder™
- Cas9 / Cas12a / Cas13a Nucleases
- Base and Prime Editing Nucleases
- GMP Cas9 Nucleases
- CRISPR sgRNA Synthesis
- HDR Knock-in Template
- CRISPR Gene Editing Kits and Antibodies
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Anti-Camelid VHH]() MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
-
![ELISA Kits]() ELISA Kits
ELISA Kits
-
![Precast Gels]() SurePAGE™ Precast Gels
SurePAGE™ Precast Gels
-
![Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System]() AmMag™ Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System
AmMag™ Quatro ProAb Automated Protein and Antibody Purification System
-
![Target Proteins]() Target Proteins
Target Proteins
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Stable Cell Lines]() Stable Cell Lines
Stable Cell Lines
-
![Cell Isolation and Activation]() Cell Isolation and Activation
Cell Isolation and Activation
-
 IVD Raw Materials
IVD Raw Materials
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
- APPLICATIONS
- RESOURCES
- ABOUT US
- SIGN IN My Account SIGN OUT
- REGISTER

![Gene Synthesis & DNA Synthesis Services Gene Synthesis & DNA Synthesis Services]()
DNA Synthesis in as Fast as 5 days
From the only company that can guarantee on-time delivery
News & Blogs » Synthetic Biology News » Four Tips for Optimizing Your PCR Amplification
Four Tips for Optimizing Your PCR Amplification
 PCR success can vary greatly depending on your experimental design. Small errors can very often result in low yield or non-specific products. Here are 4 essential tips to ensure the success of your next PCR reaction:
PCR success can vary greatly depending on your experimental design. Small errors can very often result in low yield or non-specific products. Here are 4 essential tips to ensure the success of your next PCR reaction:
Primer Design
Correct primer design is crucial for precise primer-template annealing and avoiding primer-dimer formation. Primer-dimer amplification can lead to competition for PCR reagents and inhibit your reaction.
- Avoid sequence complexity. To prevent secondary structure formation, a primer length of 18-30 nucleotides and GC content of 40-60% is recommended. Also avoid stretches of 4+ nucleotide and dinucleotide repeats.
- Check for primer homology. Any annealing between or internally within your primers will result in reduced PCR efficiency.
- Match primer Tm. Design both primers to have melting temperatures within 3°C of each other to simplify your PCR optimization.
- End with a G or C. Capping the 3' end of your primer sequence with a G or C will strengthen primer annealing at the site of extension.
- Remember to add spacers for restriction enzyme cloning/isothermal assembly. While this will not affect the efficiency of your reaction, restriction enzymes require at least 6 terminal base pairs for binding, while isothermal assembly requires a homology region of at least 15 base pairs.
- Maintain proper primer concentrations. A concentration of 0.3-1.0 µM is recommended, excessive quantities may lead to primer-dimer formation.
Template Sequence
A PCR reaction can be affected by both the quality and quantity of your DNA template.
- A "clean" template will increase reaction specificity and product yield. Be careful to avoid contamination during template extraction. Protein or chemical contamination can result in non-specific background or outright kill your PCR reaction. Check that your DNA absorbance has a 260nm/280nm ratio of ≥1.8.
- Less is more. Start small with the amount of your template to reduce the chances for non-specific annealing. We recommend using 1 ng when amplifying plasmid DNA and 100 ng when amplifying genomic DNA.
- Check the GC-content of your template. DNA templates enriched with over 60% GC-content have increased stability and may require additional reagents for separation. There are a number of GC-rich chemical enhancer options, including 5% DMSO, 1M ethylene glycol, and 0.8M 1,2-propanediol.
Reaction Reagents
While compromised reagents can affect the efficiency of your PCR reaction, most reagents hold up well with lab use. Here are the components to consider:
- DNA Polymerase- Remember to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to maintain the quality of your polymerase. An amount of 0.2-0.5 µL is recommended for most standard reaction volumes.
- dNTPs- Remember to avoid multiple freeze-thaw cycles to prevent the degradation of your dNTPs. A final concentration of between 50-200 µM is recommended, as too much can actually inhibit your PCR reaction.
- Magnesium- A concentration of 1.5-2.0 mM is recommended, but optimal conditions may vary depending on your polymerase.
Thermocycler Conditions
Thermocycler protocols and conditions are fairly standardized for PCR. Here are the three major aspects to consider:
- Modified PCR Setups- For complex primer and template sequences, consider either a hot start or touchdown PCR setup. Hot-start PCR reduces non-specific priming, by utilizing a modified polymerase, which requires an initial activation at 95°C. Touchdown PCR increases the initial annealing temperature beyond the optimal Tm, this temperature is gradually reduced in later cycles to more permissive levels. This process promotes selective amplification of the desired product.
- Annealing Temperature- We recommended setting your annealing temperature at 3°C below the melting temperature of your primer sequence melting point. When calculating melting temperature, remember to exclude any primer regions that do not anneal to the template. For future optimization, annealing temperature can be increased in 1-2°C steps.
- Extension Time- We recommend setting 1 minute of extension time per 1kb of amplicon. Optimal extension rates may depend on the processivity of the DNA polymerase.
Molecular Cloning Workflow
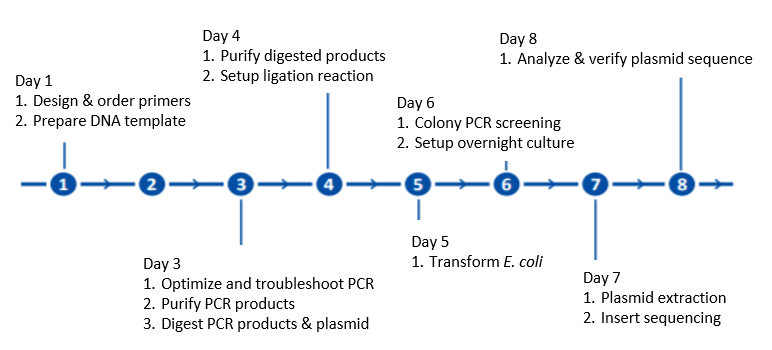
Molecular Cloning Workflow. In molecular cloning or PCR cloning, the DNA template of interest is first amplified and modified by PCR to add necessary restriction enzyme sequences. Digestion of purified DNA template and plasmid with the specified restriction enzyme(s) allows ligation of the DNA template into the open vector. Bacterial transformation supports screening of individual colonies for the desired vector containing the new DNA insert, which may be performed through sequencing following plasmid extraction.
-
Don, R., Cox, P., Wainwright, B., Baker, K. & Mattick, J. 'Touchdown' PCR to circumvent spurious priming during gene amplification. Nucleic Acids Research 19, 4008-4008 (1991).

GenBrick™ Building Blocks for Synthetic Biology
Up to 200 kb DNA sequence
New! $0.45/bp, in as few as 23 business days
Subscribe to Receive Updates
& Promotions From GenScript* We'll never share your email address with a third-party.
Latest News & Blogs
Find More Synthetic biology News
Mastering siRNA Design: Steps to Achieve Precision Gene Silencing/GenScript
Jun 23, 2025
Unlocking the Potential of Cytokines for Cancer Immunotherapy
Nov 28, 2022
From “Cold” to “Hot” Tumors with Masked Interleukin-12
Oct 14, 2022
Making CAR T Cells Safer with Synthetic Biology
Jun 12, 2022

DNA Microarrays Enable New CRISPR/Cas9-based Peptide Library Display
Sep 13, 2021

Lentiviral-Modified Cells for Rare Disease Therapy: Autologous HPSC therapy for SCID-ADA
Aug 16, 2021

-




































