HOME
-
REAGENT SERVICES
Hot!
-
Most Popular Services
-
Molecular Biology
-
Recombinant Antibody/Protein
-
Reagent Antibody
-
DNA Mutant Library
-
IVT RNA and LNP Formulations
-
Oligo Synthesis
-
Peptides
-
CRISPR Gene Editing
-
Cell Engineering
-
- Custom Peptide Synthesis
- Catalog PeptidesHot!
- Neoantigen PeptideHot!
- Cosmetic Peptide Synthesis
- Peptide Modification
- Cyclic Peptide New!
- Peptide Applications
- Peptide Library
- Peptide Drug Conjugates Service New!
- cGMP Peptide Synthesis New!
- AccuPep+ QC
- Peptide Technology & Resource
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonist ServicesNew!
-
- Cas9 sgRNA Synthesis Service
- Cas12a (cpf1) crRNA Synthesis Service
- pegRNA Synthesis Service
- HDR Templates 30% off ssDNA!
- CAR-T Knock-in Optimization Kit
- cGMP sgRNA
- cGMP HDR Templates
- CRISPR Plasmids
- CRISPR gRNA Plasmid Library
- CRISPR Cell Engineering
- Microbial Genome Editing
- sgRNA + HDR Design Tool New!
- CRISPR/Cas Protein Production New!
-
-
PRODUCTS
-
Most Popular Products
-
CRISPR Gene Editing
-
Antibodies
-
ELISA Kits
-
Protein Electrophoresis and Blotting
-
Protein Purification
-
Proteins
-
Molecular Biology
-
Stable Cell Lines
-
Cell Therapy
-
 Diagnostics
Diagnostics
-
Resources
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
AmMag™ Quatro automated plasmid purification
-
![Cas
Nucleases]() Cas Nucleases
Cas Nucleases
-
![Anti-Camelid
VHH]() MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
MonoRab™ Anti-VHH Antibodies
-
![AAV2 and AAVX Titer Capsid ELISA Kits]() AAV2 and AAVX Titer Capsid ELISA Kits
AAV2 and AAVX Titer Capsid ELISA Kits
-
![Precast Gels]() Precast Gels
Precast Gels
-
![Protein
Isolation &
Purification]() Protein Isolation & Purification
Protein Isolation & Purification
-
![Recombinant Cytokines]() Recombinant Cytokines
Recombinant Cytokines
-
![AmMag™ Quatro Automated Plasmid Purification]() AmMag™ Quatro Customer Testimonial
AmMag™ Quatro Customer Testimonial
-
![Claudin 18.2]() Claudin 18.2
Claudin 18.2
-
![Cell Isolation]() Cell Therapy Comprehensive Product Solutions
Cell Therapy Comprehensive Product Solutions
-
 cPass™ Technology RUO Kit
cPass™ Technology RUO Kit
-
![Quick
Order]() Quick Order
Quick Order
-
![Endotoxin
Detection &
Removal
System]() Endotoxin Detection & Removal System
Endotoxin Detection & Removal System
-
- APPLICATIONS
- RESOURCES
- ABOUT US
- SIGN IN My Account SIGN OUT
- REGISTER
















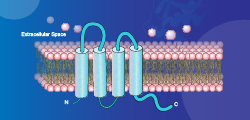

























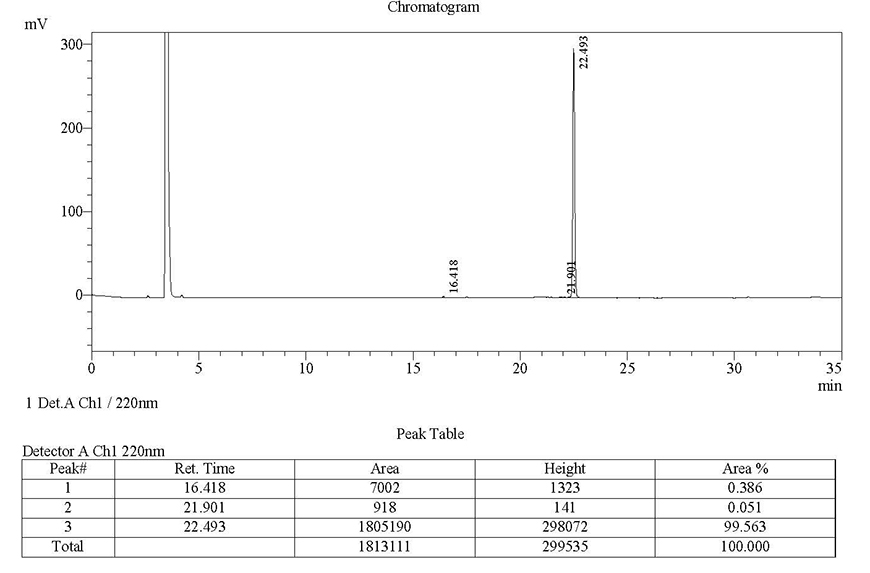
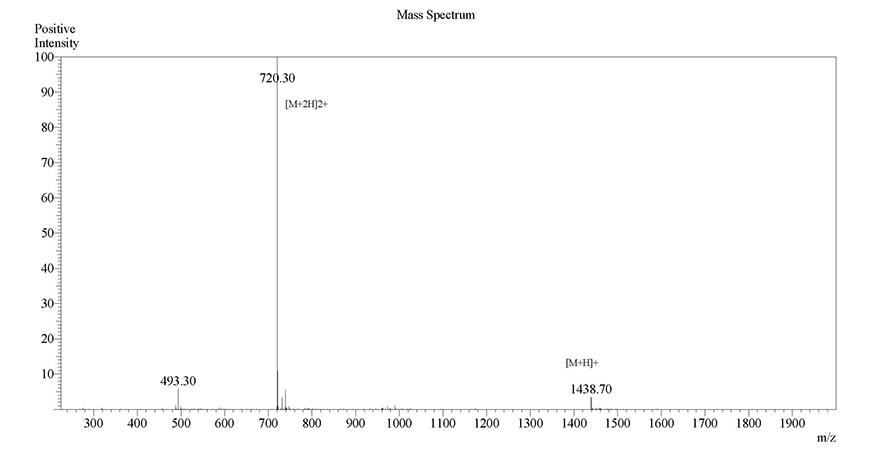
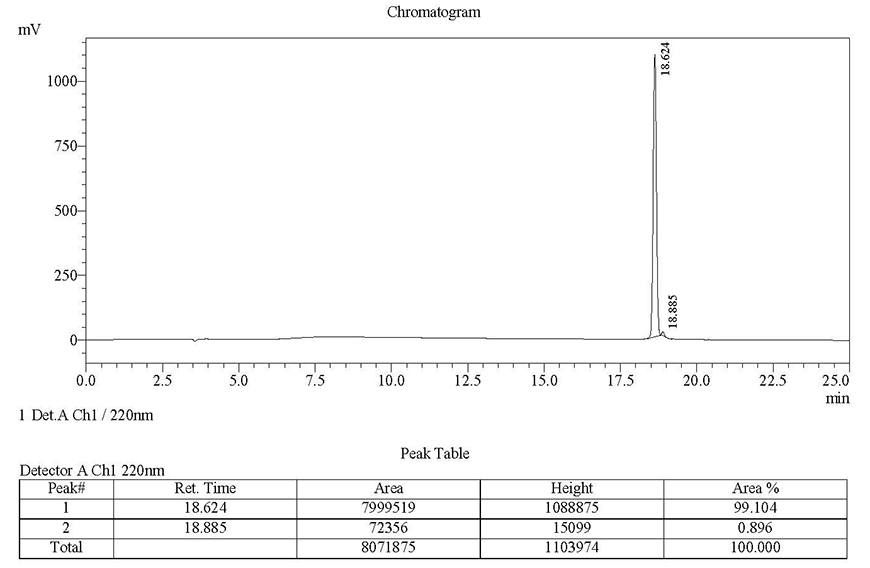
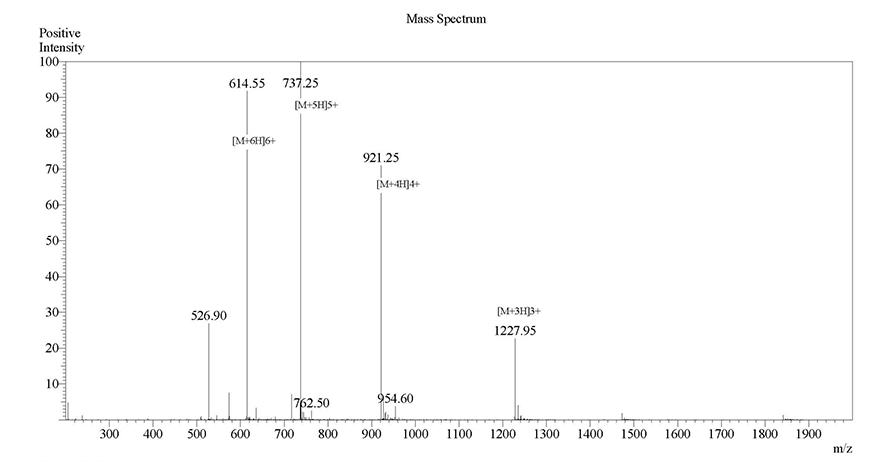
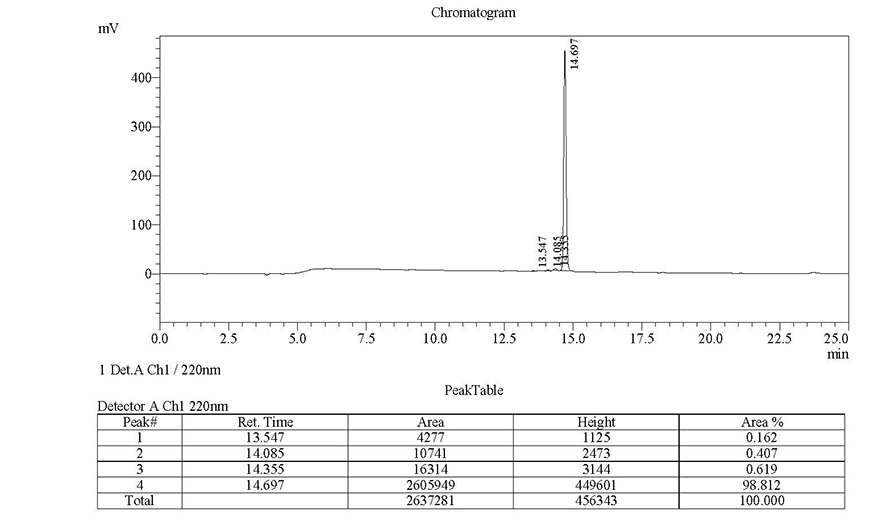
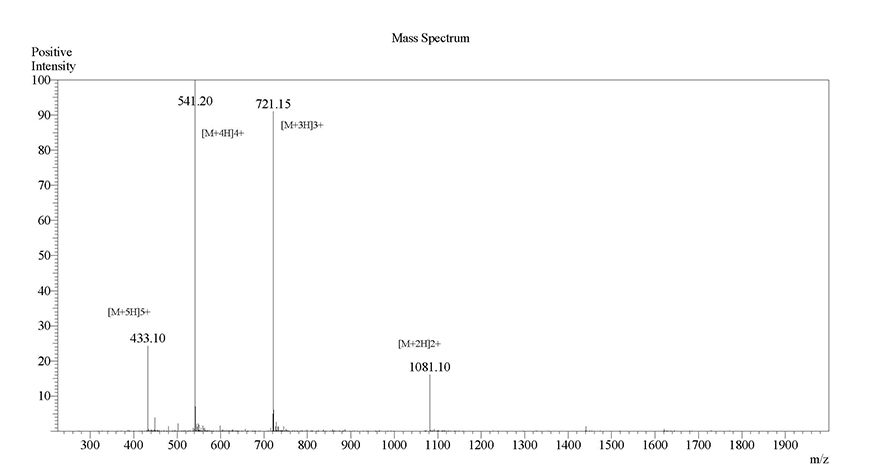

 next to the
desired modification or indicate the modification in the comments
section on the secure
next to the
desired modification or indicate the modification in the comments
section on the secure