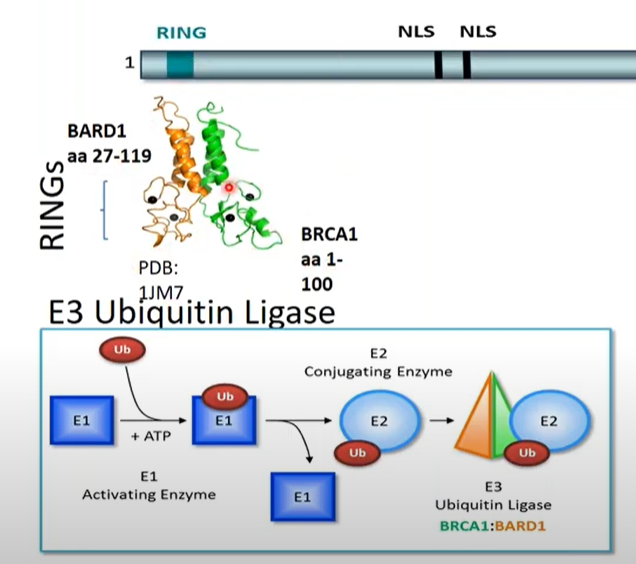
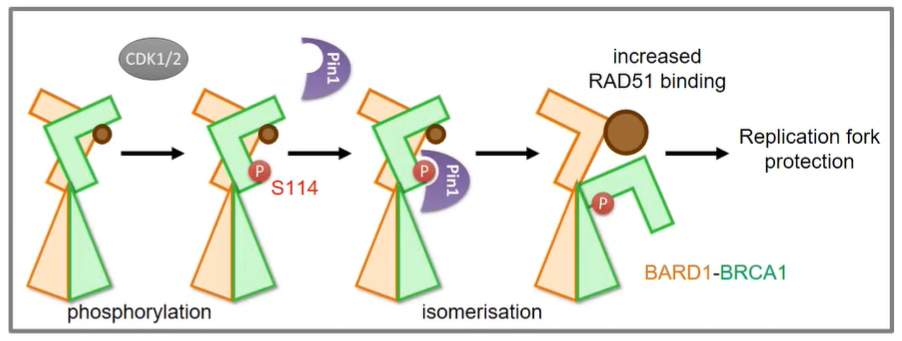
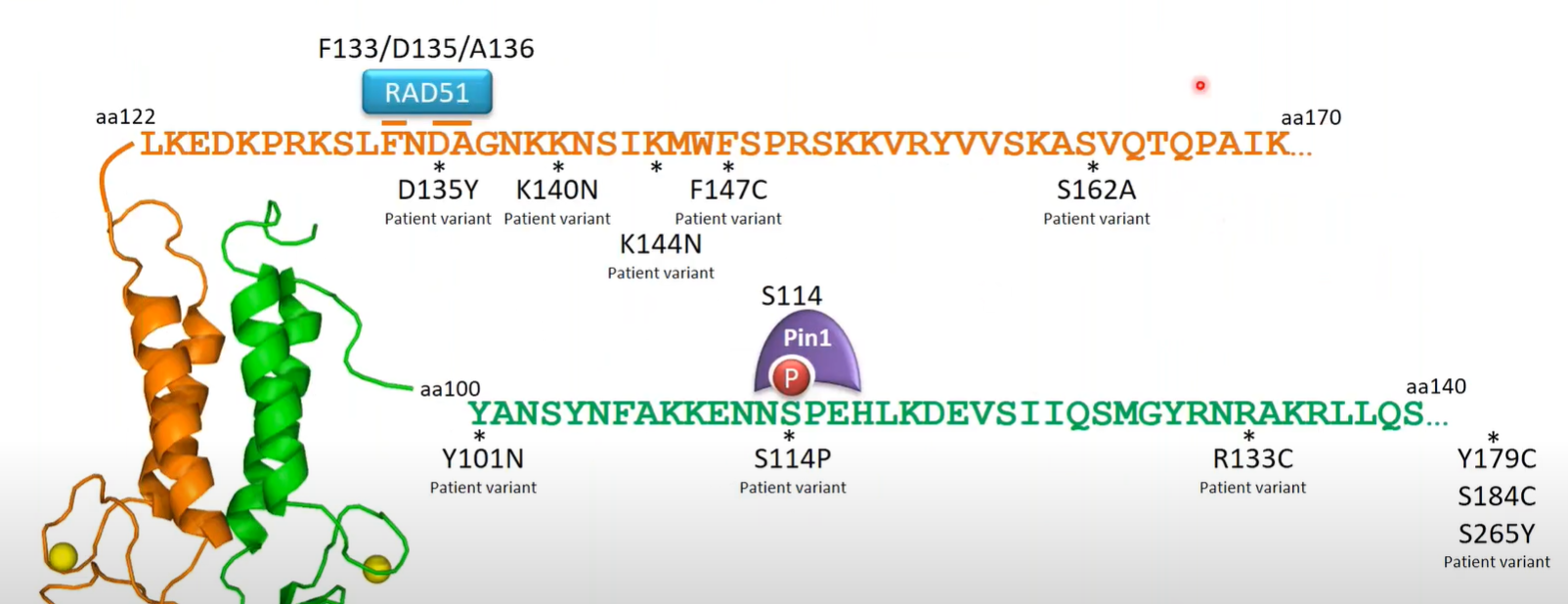
1.BRCA1 RING domain- found in the N-terminus, is the ring coordinating around two zinc ions and known to interact with BARD1. Together, BRCA1 and BARD1 form an E3 ubiquitin ligase. Mutation of BARD1 at R99, interrupts the ability of BRCA1/BARD1 to interact with the ubiquitin loaded onto E2 and reduces the rate of ubiquitin transfer to lysines of substrate proteins. Interestingly, the R99E mutation specifically affects BARD1’s ligase activity but does not affect BRCA1:BARD1 heterodimer formation, stability or BRCA1 localization to IR foci. However, the BARD1-R99E mutation affects the placement of 53BP1 relative to BARD1 and BRCA1 within DNA repair foci. Surprisingly, when tested in vitro by incubating cells with nucleotide analogs followed by treatment with hydroxyurea to induce fork stalling, the BARD1 R99E mutation does not affect replication fork protection.